Figure 7.
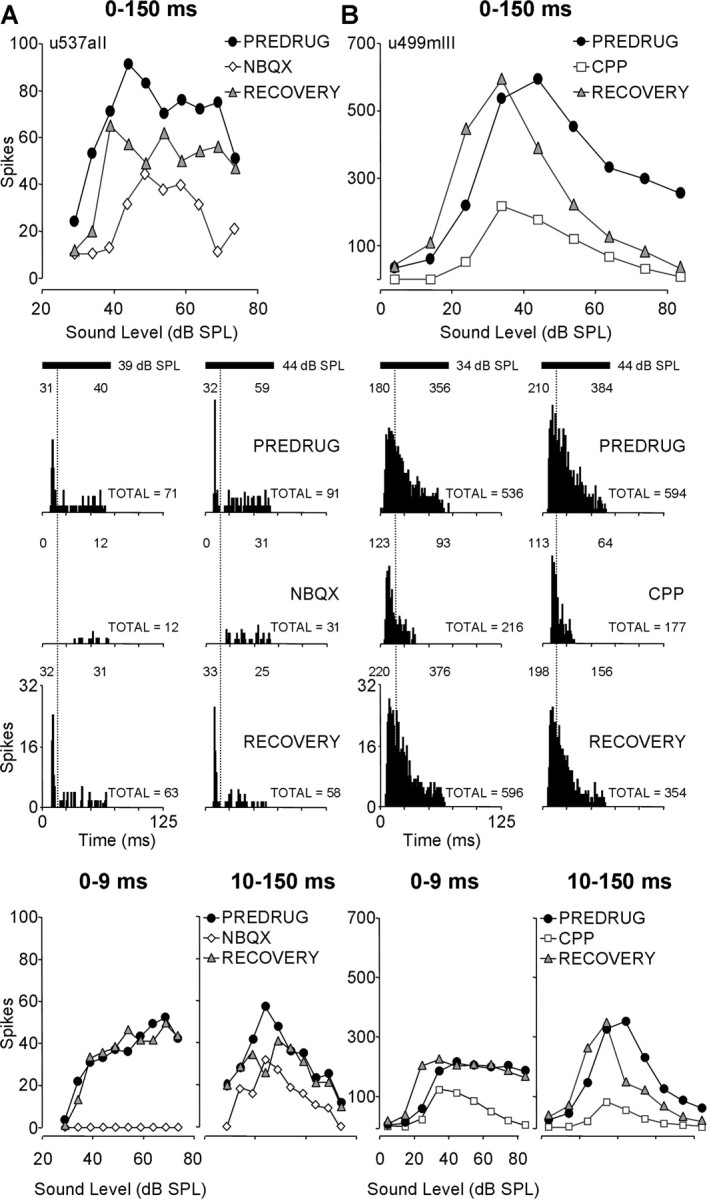
Blockade of glutamate receptors differentially affected early and late components of some sustained units. In two units, drug effects were analyzed for early (0–9 ms) and late (10–150 ms) response components. A, NBQX primarily blocked early spikes in this IC unit. BF, 57.9 kHz; MT, 39 dB SPL; minimum latency, 8.1 ms. The rate-level function of an entire response (0–150 ms; top), PSTHs (middle), and rate-level functions of early (0–9 ms) and late (10–150 ms) components (bottom) relative to the beginning of response are shown. B, CPP blocked later spikes more effectively in this unit (BF, 57.9 kHz; MT, 14 dB SPL; minimum latency, 10.2 ms), although CPP substantially reduced early spikes at higher sound levels. Vertical dotted lines in PSTHs separate early and late spikes. Numbers at the bottom right of each PSTH represent total spikes for a 150 ms time window; numbers in windowed regions above PSTHs separately display spike counts for early and late excitation. Drug application times and currents are as follows: in A, NBQX, 18 min, −80 nA; RECOVERY, 10 min; in B, CPP, 12 min, −40 nA; RECOVERY, 11 min. See Figure 2 for protocol. SPL, Sound pressure level.
