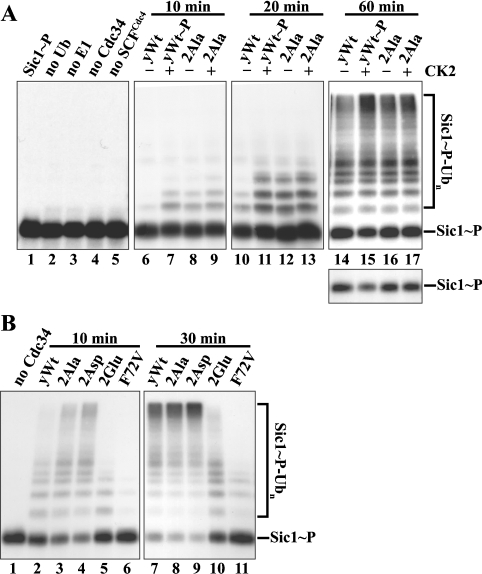
Figure 4. The phosphorylation sites of yeast Cdc34 are important for Sic1 ubiquitination in vitro.
(A) Phosphorylation of recombinant yCdc34 by CK2 enhances SCFCdc4-mediated ubiquitination of Sic1. To monitor Sic1 ubiquitination, SCFCdc4 complexes were supplemented with E1, ubiquitin, ATP, phosphorylated, 32P-labelled Sic1 (lane 1), and yeast wild-type Cdc34 (yWt), which was pre-incubated in the absence (–) or presence (+) of CK2. Prior to ubiquitination, CK2 was inhibited by 2 μM heparin. As controls, the phosphosite mutant 2Ala was subjected to the same treatment (lanes 8, 9, 12, 13, 16 and 17) and single components were omitted from the reaction (lanes 2–5). After incubation for 10, 20 or 60 min at 26 °C, proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE and visualized by autoradiography. The lower panel shows a shorter exposure of the unconjugated Sic1-P substrate remaining. (B) Mutation of the phosphorylation sites of recombinant yCdc34 alters SCFCdc4-mediated ubiquitination of Sic1. Yeast wild-type Cdc34 (yWt; lanes 2 and 7), the phosphosite mutants 2Ala (lanes 3 and 8), 2Asp (lanes 4 and 9), 2Glu (lanes 5 and 10) or the point mutant yCdc34(F72V) (lanes 6 and 11) were assayed as in (A), except that incubation times were 10 and 30 min. As a control, yCdc34 was omitted from the reaction (lane 1).