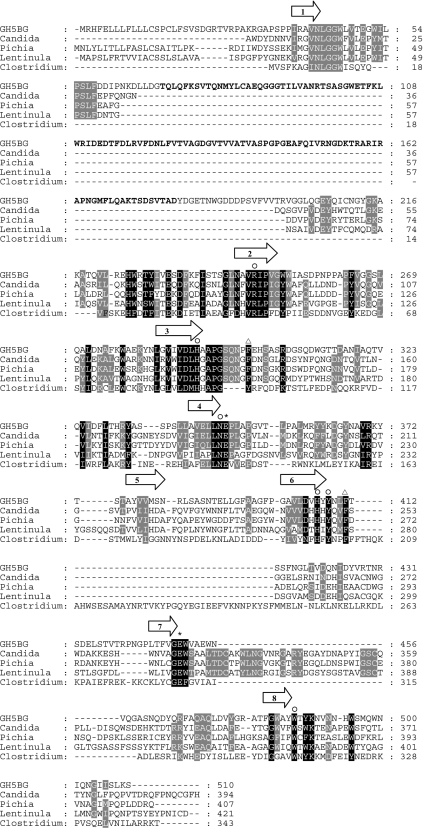
Figure 1. Alignment of the protein sequence of rice GH5BG with exo-β-1,3-glucanases and endo-β-1,4-glucanase.
GH5BG is rice GH5BG, Candida is exo-β-(1,3)-glucanase from Candida albicans (AC CAA39908), Lentinula is exo-β-(1,3)-glucanase from Lentinula edodes (AC AB192344), Pichia is exo-β-(1,3)-glucanase from Pichia pastoris (AC AY954499), and Clostridium is endo-β-(1,4)-glucanase from Clostridium thermocellum (AC AAA23220). The alignment was generated with the ClustalX implementation of ClustalW [27,28] and analysed and manually adjusted with Gendoc [29]. Alignment of the C. thermocellum sequence relied on the structural alignment of the 1CEC structural model with the C. albicans Exg 1CZ1 structure. The positions of the β-strands of the central (β/α)8 barrel are indicated by arrows above the alignment. The asterisks identify the two catalytic glutamate residues, the invariant GH family 5 residues are marked by the symbol ○ above the column, and the black and grey shadings highlight other identities between sequences. The two phenylalanine residues found at the +1 subsite of C. albicans Exg are marked by triangles above the column. The region of rice GH5BG homologous with fascin is indicated by bold text.