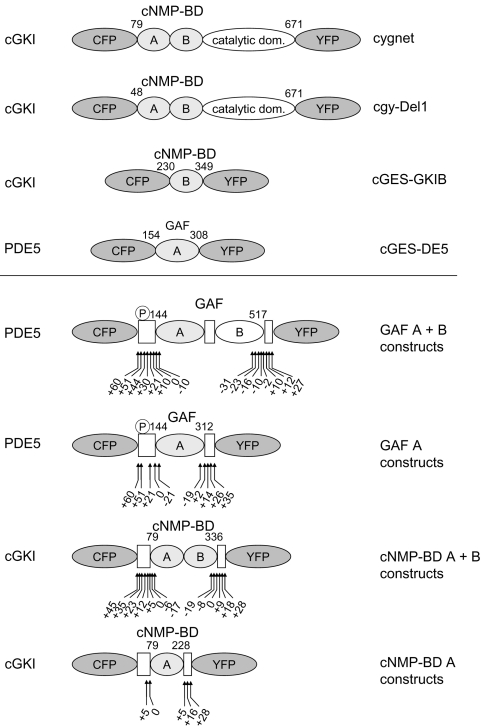
Figure 1. Schematic domain structure of cGMP indicators.
All indicators are composed of a fragment of a cGMP-binding protein sandwiched between CFP and YFP. Shown are the cGMP sensors already described (upper panel) and the ones described in this manuscript (lower panel). The cGMP-binding proteins that the indicators were derived from are stated on the left; the name of the sensor is on the right. The sensors contain the cGMP-binding sites cNMP-BD (cGKI) or GAF (PDE5), either as a single site A or B or as tandem of A+B. The numbers indicate the N- and C-terminal amino acids of the cGMP-binding domain used. The first cGMP sensors, ‘cygnet’ and ‘cgy’, were derived from cGKI with only 78 or 47 N-terminal amino acids deleted. cGES-GKIB and cGES-DE5 were generated from a single cGMP-binding site of either cGKI or PDE5 respectively. The general design of the constructs characterized in this manuscript is given in the lower panel. The boxes represent the regions of the parent proteins adjoining the cGMP-binding domains. From PDE5, either the tandem GAF A+B domains or the isolated GAF A domain were used and shortened or elongated by the amino acids indicated by the arrows. The same strategy was applied to the cNMP-BD of cGKI, and a range of different constructs was created, as indicated by the arrows. The PDE5 phosphorylation site is indicated by ℗.