Figure 1.
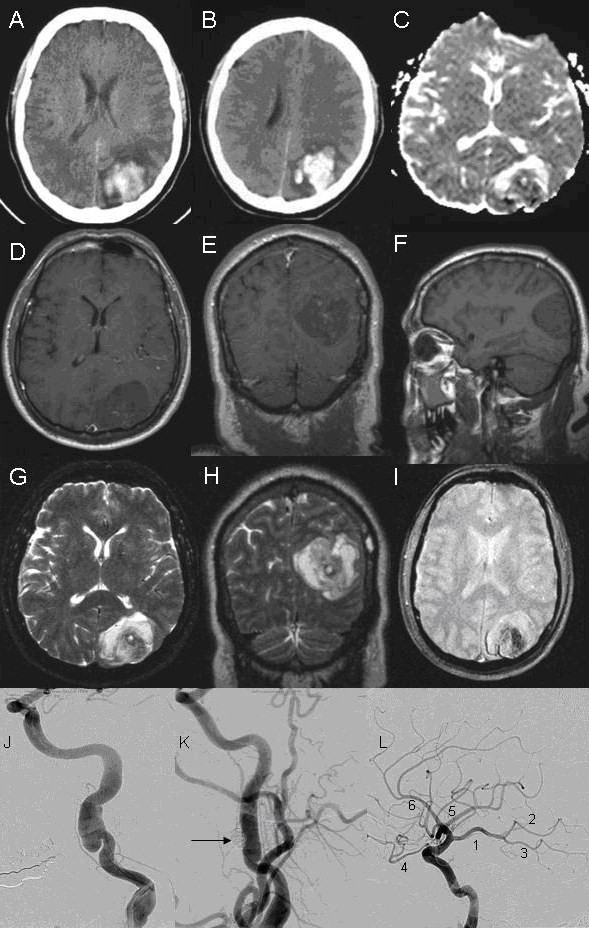
Neuroimaging of patient with occipital hemorrhage secondary to carotid dissection. A-B: Computerized tomography (CT) of the head showing left occipital hemorrhage. C: Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI). D, E, F: Axial, coronal, and sagital T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). G, H: Axial and coronal T2-weighted MRI. I: Gradient echo. J, K, L: Angiogram of left carotid artery. J: Left carotid angiogram showing pseudoaneurysm. K: Left carotid angiogram after deployment of coil (arrow) into pseudoaneurysm. L: Left internal carotid artery (ICA) angiogram with branches. 1: Fetal origin posterior cerebral artery (PCA) from ICA. 2–3: Anterior and posterior branches of PCA, respectively. 4: Ophthalmic artery. 5: Middle cerebral artery. 6: Anterior cerebral artery.
