Figure 1. Centrosome overduplication is present in high-risk HPV-associated anal neoplasms.
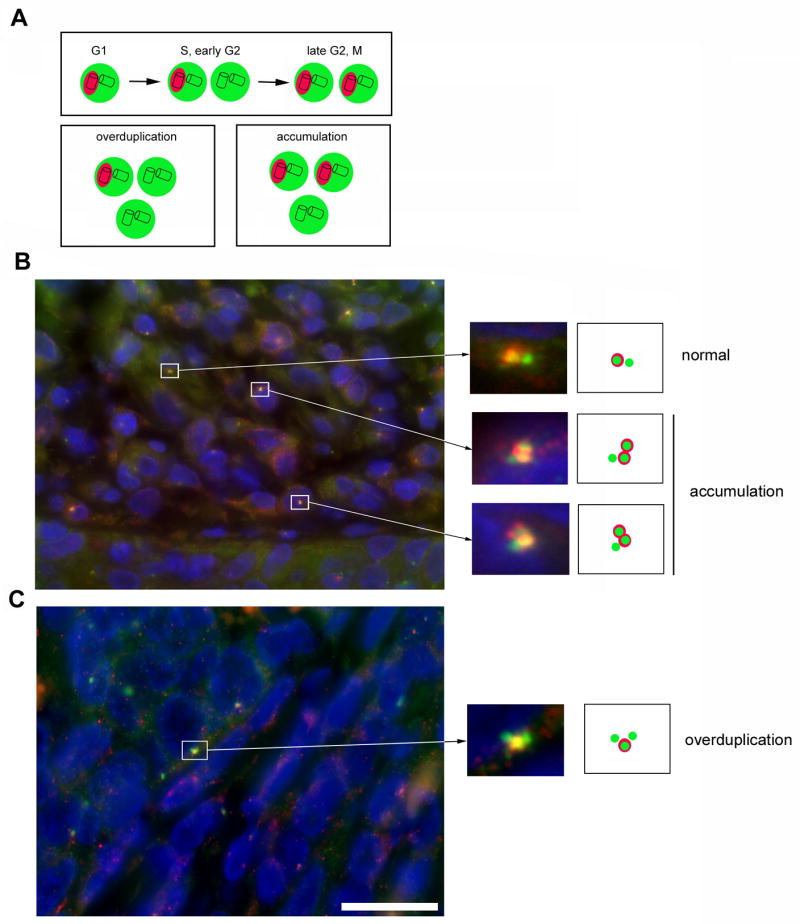
(A) Schematic overview of normal centrosome duplication and pathways that can lead to centrosome amplification. The PCM is in green whereas Cep170-positive centrioles are highlighted in red. Note that during centrosome overduplication in S or early G2 phase of the cell division cycle, only a single centrosome should contain a mature mother centriole that is positive for Cep170.
(B,C) Examples of normal centrosome duplication, centrosome accumulation and centrosome overduplication in two HSILs that contained high-risk HPV DNA. The tissue samples were analyzed by co-immunofluorescence microscopy for the PCM marker γ-tubulin (green) and Cep170 (red). Note the excessive Cep170 staining that may hint to a deregulation of Cep170 expression in HPV-associated neoplasms. Nuclei stained with DAPI. Scale bar indicates 25 μm.
