Figure 2.
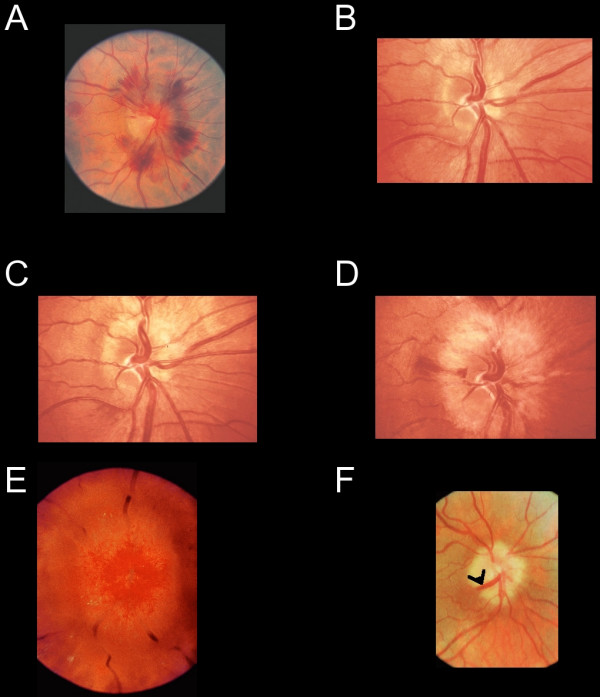
Funduscopic signs of high intracranial pressure. (A) The disc shows florid hemorrhages with relatively little swelling, indicating a rapid, dramatic increase in CSF pressure. Progressive changes of optic disc oedema are seen in a patient with an intracranial tumour who declined treatment (B-D). (B) Early nerve fiber dilatation is seen particularly superiorly, inferiorly and nasally. (C) This increases and venous engorgement develops. (D) Temporal nerve fiber dilatation and swelling of the disc increases and hemorrhages appear. (E) In gross chronic disc oedema the normal retinal vasculature is masked and dilated superficial capillaries are observed. (F) In atrophic optic disc oedema nerve fibers are eventually destroyed and the optic disc without viable nerve fibers does not swell. This patient had longstanding benign intracranial hypertension. Retinochoroidal venous collaterals are present (black arrowhead). (All images are reprinted from reference 17, with permission).
