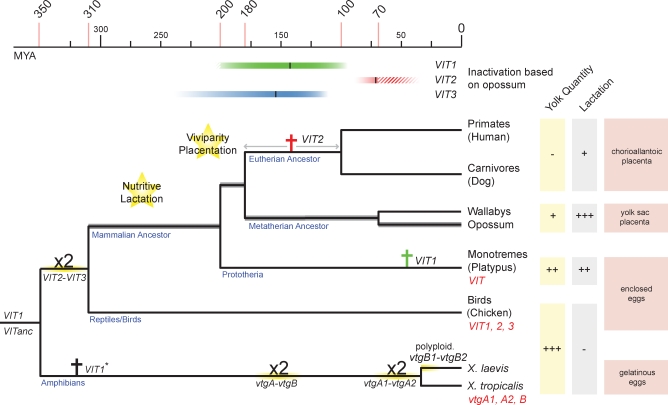
Figure 1. VIT Gene Evolution in Tetrapods.
The topology and divergence times of the tree are based on previous studies [19,24,25,41]. Latin crosses indicate VIT inactivation events in eutherians and monotremes. Inactivation estimates (including approximated 95% prediction intervals) based on opossum VIT sequences are indicated by colored bars at the top (see also Figure 3). Duplications (“x2”) are indicated. VITanc is the likely ancestor of both the amphibian vtgA1/vtgA2 and VIT2/VIT3 genes in birds. Functional VIT genes in extant species are indicated in red. The inactivation time of VIT1* on the amphibian branch could not be estimated because of its absence in Xenopus tropicalis.