Figure 2.
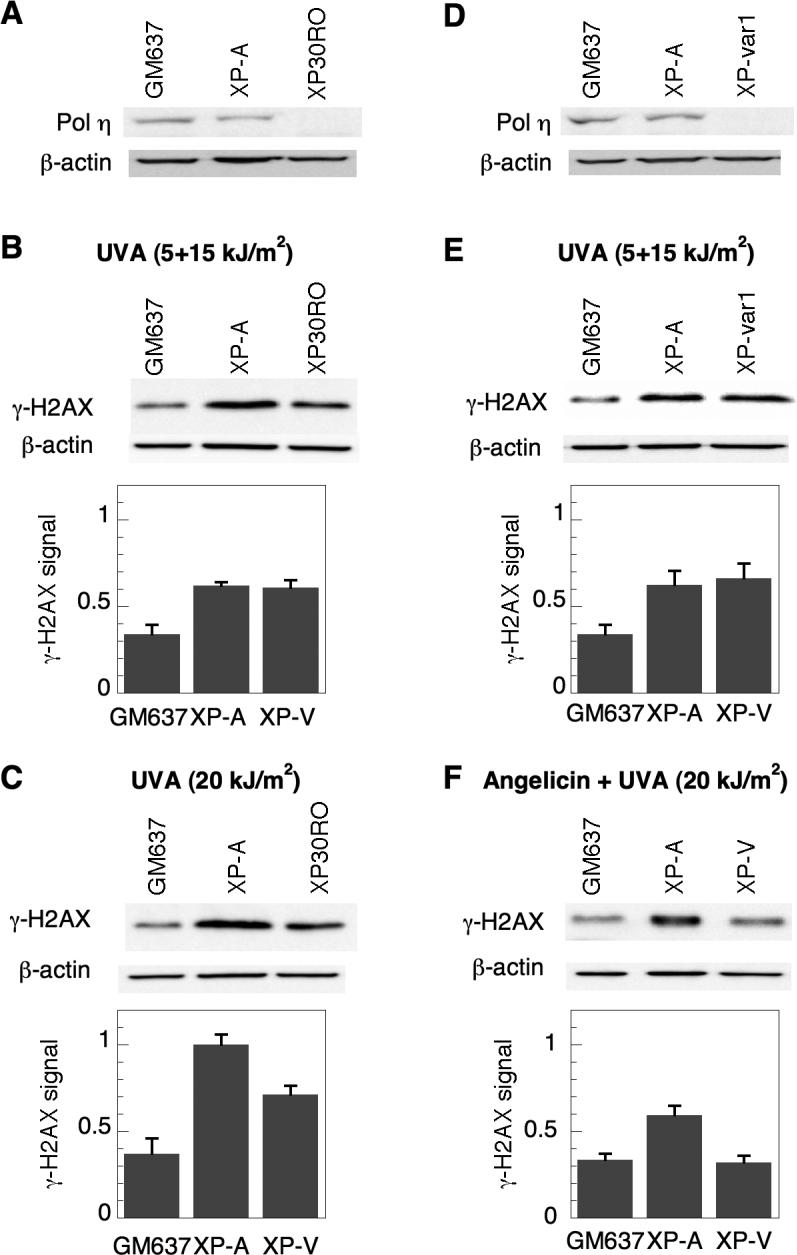
Induction of γ-H2AX in XP-A and XP-V cells following psoralen photoadducts. A) pol η expression was analyzed by Western immunoblotting in GM637, XP-A (XP12RO) and XP-V (XP30RO) cells. B) Cells were treated with 10 μM HMT and split-dose UVA, incubated in media for 3 hours, and analyzed by Western immunoblotting for γ-H2AX expression. C) Cells were also treated with 10 μM HMT and continuously irradiated with 20 kJ/m2 UVA. Identical experiments were performed with a separate XP-V cell line (XPvar-1) and compared to GM637 and XP-A cells to assess D) pol η expression, and E) γ-H2AX expression following treatment with HMT and split-dose UVA. F) γ-H2AX expression following angelicin and UVA. GM637, XP-A and XP-V (XP30RO) cells were treated with 10 μM angelicin and irradiated with 20 kJ/m2 UVA, allowed to incubate for 6 hours, and then harvested for Western immunoblotting to detect and quantify γ-H2AX and β-actin levels. Actin served as a loading control in all experiments. Error bars in graphs denote standard deviation.
