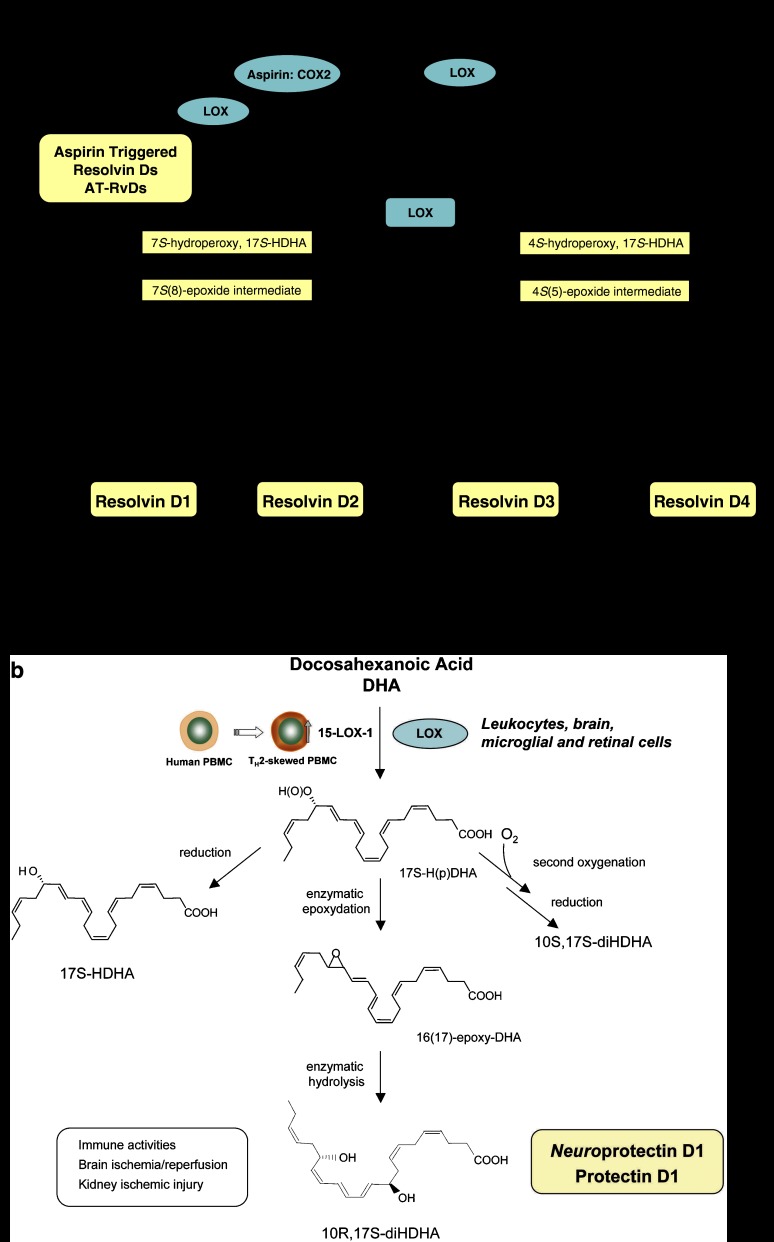
Figure 3.
D-series resolvins and protectins. (a) Resolvin Ds: formed from docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), the proposed biosynthetic pathways reconstructed in vitro involve the lipoxygenase (LOX) product 17S-H(p)DHA, which is rapidly transformed by the LOX activity in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN) into two epoxide intermediates. These two novel epoxide intermediates open to form bioactive products denoted 17S-resolvin D series (RvD1-4). Aspirin also impacts the formation of resolvin D series by catalytically switching COX-2 to a 17R-lipoxygenase-like mechanism that generates 17R-H(p)DHA, and subsequently 17R-resolvin D series (AT-RvDs). (b) Protectins: the initial enzymatic product 17S-H(p)DHA is converted to neuroprotectin D1/PD1. The complete stereochemistries of the bioactive mediators and related natural isomers are established (see text for further details).