Fig. 4.
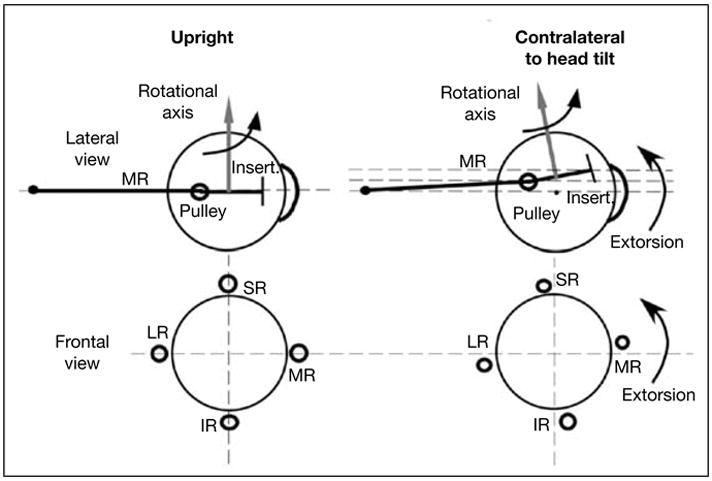
Diagram of effects of head tilt on rectus pulleys in lateral (top row) and frontal (bottom row) views. With head upright, the IR, LR, MR, and SR pulleys are arrayed in frontal view in a cruciate pattern. The MR passes through its pulley, represented as a ring, to its scleral insertion. The rotational velocity axis imparted by the MR is perpendicular to the segment from pulley to insertion. The pulley array extorts during contralateral head tilt. Since during head tilt the MR pulley shifts superiorly by the half the distance the insertion shifts, the MR’s velocity axis changes by one fourth the ocular torsion. By permission from Demer and Clark [69].
