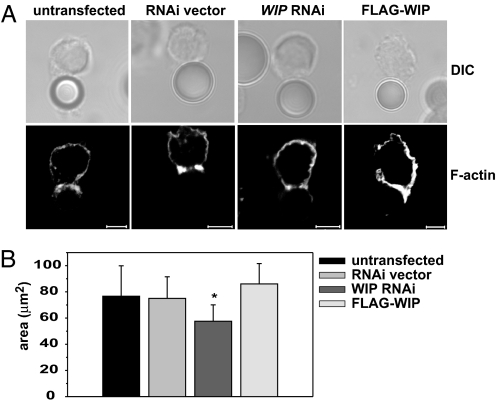
Fig. 4.
WIP knockdown does not prevent F-actin polarization, but affects the area of F-actin accumulation at the cell–cell interface. (A) F-actin accumulation at the cell–bead interface. YTS cells either untransfected or transfected with empty RNAi vector, WIP RNAi, or FLAG-WIP were mixed with anti-LFA1 mAb-coated polystyrene beads for 60 min at 37°C. The cells were then stained with AlexaFluor 568-conjugated phalloidin to visualize F-actin. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (B) The area of F-actin accumulated at the cell–cell contact site. Untransfected YTS cells or YTS cells transfected with empty RNAi vector, WIP RNAi, or FLAG-WIP were mixed with 721.221 target cells 10 min at 37°C, followed by staining with AlexaFluor 568-conjugated phalloidin and AlexaFluor 647-conjugated anti-perforin antibodies (to distinguish NK cells from target cells). F-actin at the immune synapse was visualized by taking a series of images of conjugated cells in the z plane, from which the area of F-actin accumulation was measured. n ≥ 14. Error bars represent SD. The asterisk indicates statistical significance (P < 0.05 by Student's t test) when compared with control.