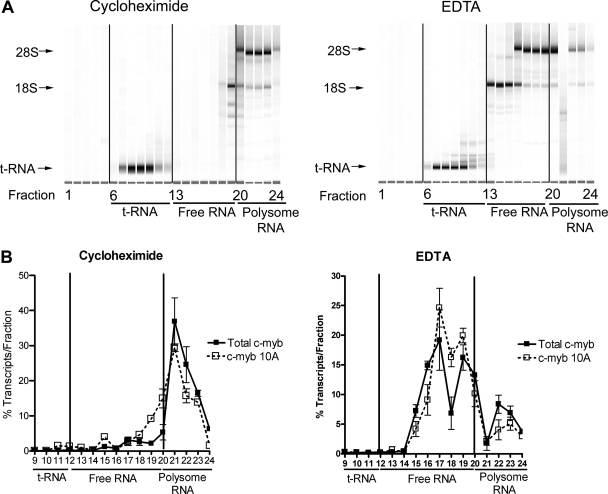
FIG. 5.
The c-myb splice variants associate with polysomes. Cytoplasmic extracts isolated from K562 cells were fractionated on Nyzode density gradients containing cycloheximide (to inhibit polysome-RNA dissociation) or EDTA (to release polysomes from RNA). The gradients were separated into 24 fractions (fraction 1, top; fraction 24, bottom). (A) RNA profiles. RNA samples isolated from the gradients containing cycloheximide (left panel) or EDTA (right panel) were analyzed as described in Materials and Methods. Fractions 20 to 24 contained polysomes, as indicated by the presence of both the 18S and 28S rRNAs. Non-polysome-associated RNA was present in fractions 13 to 19, between the tRNA in fractions 7 to 12 and the ribosome-containing fractions. Note the shift toward lower-density fractions for the 18S ribosomal subunit in the EDTA gradient (compare fractions 13 to 19 in EDTA and cycloheximide gradients), confirming that the EDTA treatment disrupted the polysomes. (B) Results from qPCR analysis. Relative total c-myb transcript levels or levels of transcripts containing exon 10A were detected in the gradient fractions by qPCR. Copy numbers of each transcript were determined using plasmid standard curves. The plots show the percentages of transcripts recovered from each fraction. Note the shift in both total c-myb and exon 10A transcripts in the EDTA gradient. Nearly identical results were obtained for transcripts containing exons 8A, 9A, 9B, 13A, and 14A (not shown).