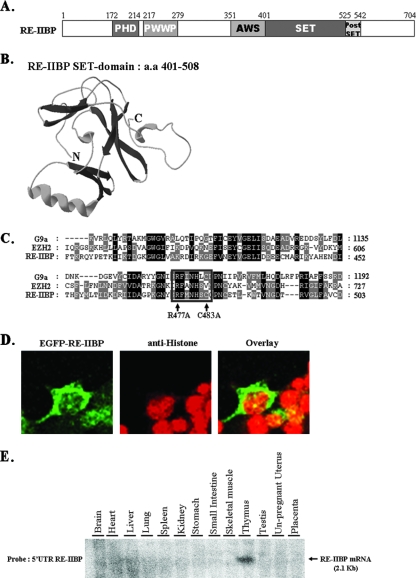
FIG. 1.
Structural features of the RE-IIBP. (A) Schematic view of RE-IIBP domains: amino acids 172 to 214 were predicted to be the PHD domain; amino acids 217 to 279 were predicted to be the PWWP (proline-tryptophan-tryptophan-proline) domain; amino acids 401 to 525 were predicted to be the SET domain; and amino acids 526 to 542 were predicted to be the postSET domain. (B) Three-dimensional modeling of RE-IIBP SET domain was performed by using the stand-alone Swiss-PdbViewer with an installed protein loop database. (C) Multiple alignments of the SET domains of G9a, EZH2, and RE-IIBP proteins. RE-IIBP protein harbors an RΦΦNHSC motif (where Φ indicates a hydrophobic residue; boxed). The arrows indicate the R477 and C483 residues of the RΦΦNHSC motif that are mutated for testing the HMTase activity of RE-IIBP protein. Conserved amino acid residues between three sequences are shown in black, and similar residues between these two sequences are shaded in gray. (D) HeLa cells were transfected with enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP)-RE-IIBP, stained with anti-histone antibodies, and detected with Cy3-conjugated secondary antibodies. (E) The adult human tissue blot was hybridized to a 32P-labeled 5′ UTR RE-IIBP DNA probe. The 2.1-kb RE-IIBP mRNA transcript is indicated by an arrow.