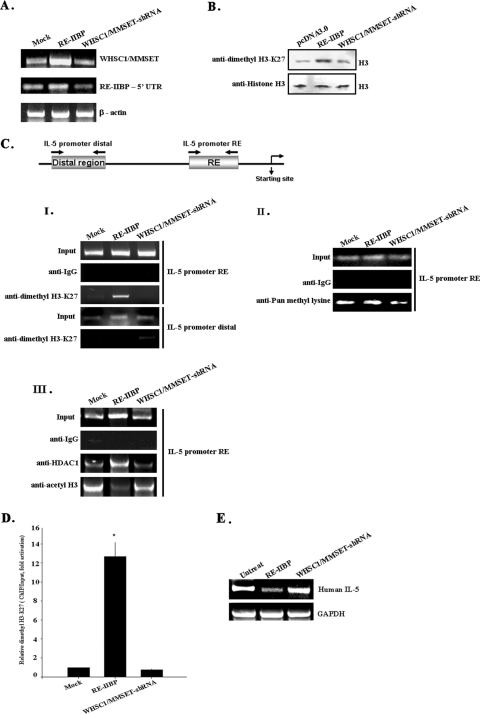
FIG. 5.
Effects of RE-IIBP transcript by RNA interference. (A) HeLa cells were mock transfected or transfected with pcDNA3.1-HisTOPO-RE-IIBP and pSM2c-WHSC1/MMSET-shRNA, and WHSC1/MMESET and RE-IIBP expression levels were confirmed by RT-PCR with specific primers. (B) The status of lysine methylation was determined using transiently transfected cells with RE-IIBP and WHSC1/MMSET-shRNA. Transfected cells were lysed and immunoblotted with anti-dimethyl H3-K27 antibodies. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with the pcDNA3.0, pcDNA3.1-HisTOPO-RE-IIBP, and pSM2c-WHSC1/MMSET-shRNA. Following transfection, ChIP assays were performed employing control IgG, anti-dimethyl H3-K27 (I), anti-pan methyl lysine antibodies (II), and anti-acetyl H3 and anti-HDAC1 antibodies (III). The immunoprecipitated DNA fragments were amplified by PCR from the proximal and distal promoter regions of the integrated IL-5. (D) ChIP analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies and examined by qPCR in the presence of proximal IL-5 promoter fragments. The dimethyl H3-K27 level was normalized by input. (E) Total RNA was isolated from HeLa cells. RT-PCR analysis was performed with primers for IL-5. Human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as an RNA loading control. The relative levels of gene expression of RE-IIBP mRNA in untreated cells and RE-IIBP- and WHSC1/MMSET-shRNA-transfected cells were compared by RT-PCR.