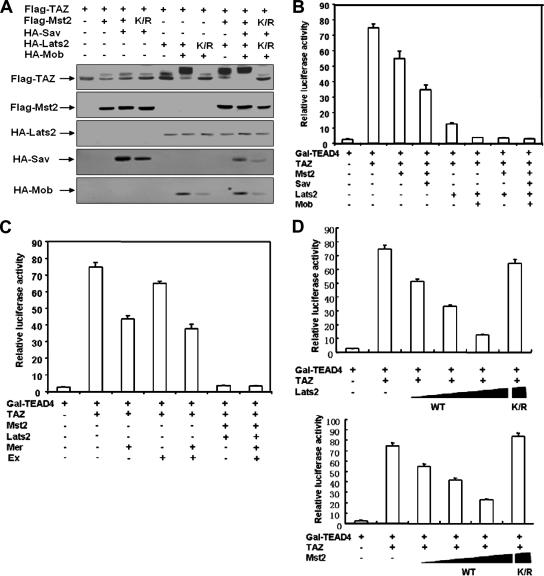
FIG. 1.
The transcription coactivator activity of TAZ is inhibited by the Hippo pathway. (A) The cotransfection of Mst2 and Lats2 decreases TAZ electrophoretic mobility. Flag-TAZ was cotransfected with the indicated plasmids into BOSC cells (a cell line derived from HEK 293), and Western blotting was employed to examine TAZ mobility. (B) TAZ activity is repressed by Mst2 and Lats2. The 5× GAL4 UAS-luciferase reporter and GAL4-TEAD4 were transfected into BOCS cells, with the indicated plasmids. Renilla luciferase plasmid was also cotransfected as an internal control. Firefly luciferase activity was measured and normalized to Renilla luciferase activity. Data are representative of three independent experiments. The coexpression of the Hippo pathway components Mst2, Sav, Lats2, and Mob inhibited TAZ activity. (C) TAZ activity is inhibited by human Ex and Mer. The experiments shown are similar to those shown in panel B. Both Ex and Mer cause a significant inhibition of the TAZ reporter. (D) Kinase activity is required for Mst2 and Lats2 to inhibit TAZ. Increasing amounts of wild-type Lats2 (upper panel) or Mst2 (lower panel) were cotransfected with the TAZ reporter. Both Lats2 and Mst2 show a dose-dependent inhibition of the TAZ reporter. In contrast, the kinase-inactive mutants (K/R) of both Lats2 and Mst2 cannot inhibit the TAZ reporter.