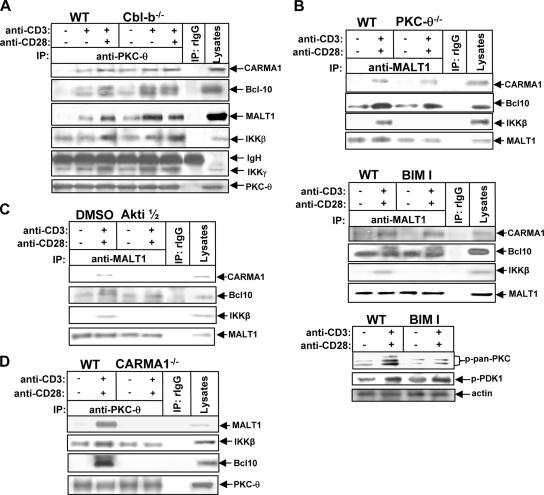
FIG. 4.
Cbl-b controls the assembly of a signaling complex consisting of PKC-θ, CARMA-1, Bcl-10, MALT-1, IKKβ, and IKKγ. (A) WT and Cbl-b−/− T cells (108/ml) were stimulated with anti-CD3 Ab in the presence or absence of anti-CD28 Ab for 15 min and lysed in 0.5% NP-40 lysis buffer. The cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-PKC-θ Ab and analyzed with anti-CARMA1, anti-Bcl10, anti-MALT1, anti-IKKβ, anti-IKKγ, and PKC-θ Abs. (B) WT and PKC-θ−/− T cells or BALB/c T cells pretreated with bisindolylmaleimide I (0.5 μM) for 15 min were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 Abs for 15 min, immunoprecipitated with anti-MALT1 Ab, and analyzed with anti-CARMA1, anti-MALT1, anti-Bcl10, and anti-IKKβ Abs, respectively. The specificity of BIM I was determined by analyzing the lysates of T cells treated with BIM I with anti-pan-phospho-PKC and anti-phospho-PDK-1 Abs, respectively. (C) BALB/c T cells were pretreated with a specific Akt inhibitor, Akti 1/2, for 15 min, stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 Abs for 15 min, and lysed. The formation of the CBM complex was determined as in B. (D) WT and CARMA1−/− T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 Abs as above, immunoprecipitated with anti-PKC-θ Ab, and analyzed with anti-Bcl10, anti-MALT1, and anti-IKKβ Abs, respectively. Data represent one of three independent experiments. −, absence of; +, presence of.