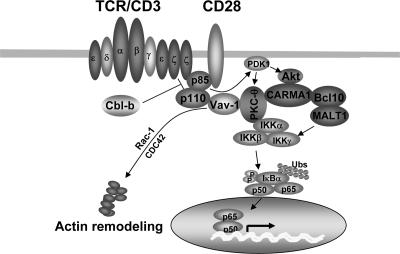
FIG. 6.
Model of Cbl-b action on T-cell activation. TCR/CD28 ligation induces the activation of several pathways, including that of PI3-K, which is targeted by Cbl-b for ubiquitination. PI3-K may activate Vav-1 through the interaction of its product PIP3 and the PH domain of Vav-1, resulting in the recruitment of Vav-1 to the plasma membrane. Vav-1 then functions as an adaptor protein to bring PKC-θ into the proximity of PI3-K and allow it to be phosphorylated by PDK-1. The formation of the CBM complex may be dependent on Akt, a downstream target of PI3-K, but independent of PKC-θ, which couples IKKs to the CBM complex, whereas CARMA1 links PKC-θ-IKKs to the Bcl10-MALT1 complex. In the absence of Cbl-b, both Akt and PKC-θ are hyperactivated upon TCR stimulation. Consequently, in Cbl-b−/− T cells, hyperactivated Akt induced by TCR stimulation initiates the enhanced formation of the CBM complex, whereas hyperactivated PKC-θ couples additional IKKs to the CBM complex, resulting in a large functional signaling complex and leading to an elevated activation of NF-κB.