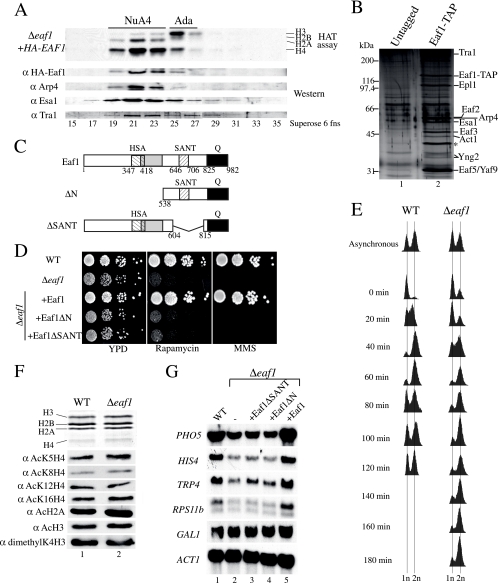
FIG. 1.
Eaf1 is found exclusively in the NuA4 HAT complex and is required for its functions but not for global histone H4/H2A acetylation. (A) Eaf1 coelutes with the HAT activity of NuA4 as well as with subunits of the NuA4 HAT complex. An extract from Δeaf1 cells harboring an episomal HA-EAF1 gene was fractionated on nickel and Mono Q columns. The desired fractions (fns) were pooled and loaded on a Superose-6 gel filtration column. Western blots show Arp4, Tra1, and Esa1 coelution with NuA4 HAT activity (fractions 19 to 23). α, anti. (B) Eaf1 is specific to the NuA4 complex. The TAP of Eaf1 shows the association with NuA4 subunits. Purified material from untagged and EAF1-TAP strains was loaded onto gradient gels and visualized by silver staining. Bands corresponding to the NuA4 subunits are indicated on the right. The asterisk corresponds to a nonspecific band known to purify with TAP-tagged protein. (C) Schematic representation of Eaf1. Eaf1 contains an HSA domain,a charged domain (gray) partially overlapping the HSA domain, and a SANT domain at the positions indicated. The C terminus of Eaf1 is enriched in glutamine (Q) (black). (D) Full-length Eaf1 is required for growth in the presence of DNA damage or crippled ribosome biogenesis. Serial 10-fold dilutions of Δeaf1, eaf1ΔN, eaf1ΔSANT, and isogenic wild-type (WT) strains were grown in the presence or absence of 0.03% MMS or 25 nM rapamycin. (E) Deletion of Eaf1 results in a slow G2/M passage. Liquid cultures of wild-type and Δeaf1 cells were blocked in G1 by the addition of α-factor. DNA content was quantified by fluorescent-activated cell sorter analysis. The 1n peak represents cells in the G1/S stage, whereas the 2n peak represents cells in the G2/M stage. (F) Deletion of Eaf1 does not affect global acetylation by NuA4. Nucleosomal histones from isogenic wild-type and Δeaf1 strains were purified and analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies indicated on the left (the top panel shows Coomassie-stained histones). (G) Eaf1 is implicated in gene-specific regulation. RNAs from isogenic wild-type, Δeaf1, eaf1ΔSANT, eaf1ΔN, and EAF1 cells were isolated, and Northern blot analyses were performed using the probes indicated on the left.