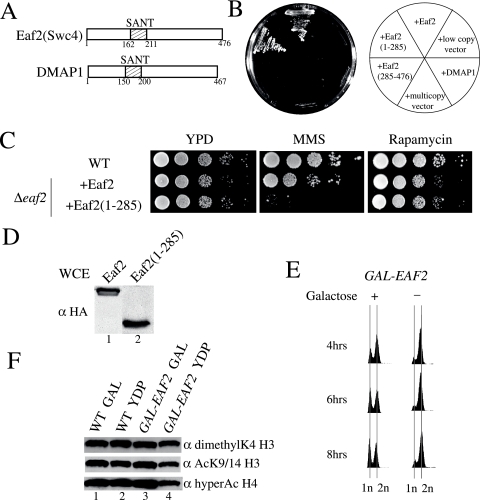
FIG. 2.
Eaf2, another SANT-containing subunit, is essential for cell viability and affects a subset of NuA4 functions. (A) Schematic representation of Eaf2 (Swc4) and human DMAP1. (B) The SANT-containing N-terminal portion of Eaf2 is essential for viability, and human DMAP1 does not complement eaf2 mutants in yeast. Strains in which the EAF2 gene has been deleted but that express an episomal version of EAF2, the truncated EAF2(1-285) or EAF2(285-476), DMAP1, or an empty vector were streaked on solid YPD medium. (C) Deletion of the C-terminal portion of Eaf2 causes sensitivity to MMS but not to rapamycin. Serial 10-fold dilutions of the indicated strains were incubated on solid YPD medium containing either 0.03% MMS or 25 nM rapamycin. (D) Episomal full-length and truncated Eaf2 are expressed at similar levels in vivo. Whole-cell extracts (WCE) from the indicated strains were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-HA (α HA). (E) Eaf2 is essential for cell cycle progression. The depletion of Eaf2 leads to cells being blocked at G2/M. Cells in which the endogenous EAF2 promoter has been replaced by the inducible GAL1 promoter were incubated in liquid medium in the presence or absence of galactose (GAL), and the DNA content was analyzed by flow cytometry. (F) Eaf2 is not essential for the global acetylation of chromatin by NuA4. Cells harboring EAF2 under the control of the GAL1 promoter as well as wild-type (WT) cells were incubated in medium containing galactose or glucose for 12 h at 30°C. Western blot analyses were performed with histones purified from those strains using the indicated antibodies.