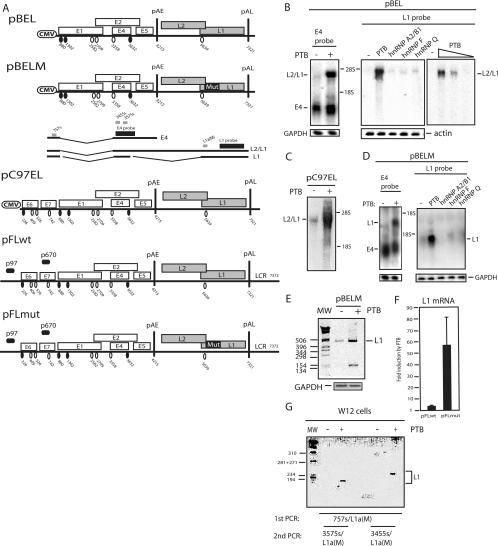
FIG. 2.
(A) Schematic representation of subgenomic HPV-16 expression plasmids used to study the induction of late gene expression by PTB. Numbers indicate the nucleotide positions of 5′ splice sites (filled circles) and 3′ splice sites (empty circles) or poly(A) sites pAE and pAL. Major potential mRNAs produced by pBEL and pBELM are indicated below the plasmids. Gray bars represent RT-PCR primers, and black bars represent E4 and L1 probes used for Northern blotting. Mut, a mutant L1 gene in which splicing silencers have been inactivated (11, 61); LCR, long control region. (B, C, and D) Northern blots of cytoplasmic RNA extracted from HeLa cells transfected with pBEL, pC97EL, or pBELM in the absence or presence of plasmids expressing PTB, hnRNP A2/B1, hnRNP F, or hnRNP Q. Blots were probed with the E4 or L1 probe as indicated. Gels were also probed for GAPDH or actin expression. The positions of the E4, L1, and L2/L1 mRNAs are indicated. +, present; −, absent. (E) RT-PCR with primers 757s and L1a(M) (see panel A) (61) on the same cytoplasmic RNA that was analyzed in the blot in panel D. GAPDH cDNA was amplified as a control. MW, molecular weight marker. (F) Real-time PCR was performed with RNA extracted from cells transfected with plasmid pFLwt or pFLmut in the absence or presence of PTB-expressing plasmid pCMVPTB1, as described in Materials and Methods. The levels of induction (n-fold) by PTB were calculated for pFLwt and pFLmut and are shown in the graph. (G) Results from nested RT-PCRs to detect HPV-16 L1 mRNA in HPV-16-containing W12 cells transfected with an empty vector (−) or with the pCMVPTB1 plasmid (+). First, PCR was performed with primers 757s and L1a(WT). This reaction was nested with either 3455s and L1a(WT) or 3575s and L1a(WT), as indicated in the figure.