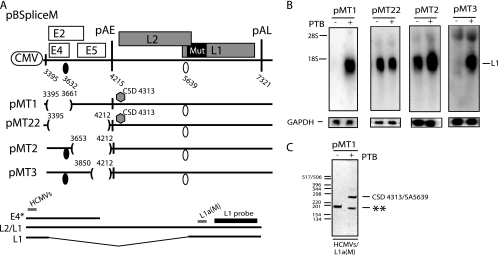
FIG. 8.
(A) Schematic representation of subgenomic HPV-16 expression plasmids pBSpliceM, pBMT1, pBMT22, pBMT2, and pBMT3. Numbers indicate the nucleotide positions of 5′ splice sites (filled circles) and 3′ splice sites (empty circles) or the positions of pAE and pAL or mark the borders of deletions. Major potential mRNAs produced by these plasmids are indicated below pBSpliceM. E4* indicates a short mRNA encoding E4 and E5 that is unspliced due to the absence of SD880 and other 5′ splice sites upstream of the major E4 3′ splice site SA3358 in the pBSplice-derived plasmids. The E4 and L1 probes used for Northern blotting are indicated. Gray bars represent RT-PCR primers HCMVS (Table 1) and L1a(M) (61). CSD indicates a cryptic 5′ splice site that was identified by the cloning and sequencing of the RT-PCR products seen in panel C. Mut, a mutant L1 gene in which splicing silencers have been inactivated (11, 61). (B) Northern blots of cytoplasmic RNA extracted from HeLa cells transfected with pMT1, pMT22, pMT2, or pMT3 in the absence or presence of a PTB-expressing plasmid. Blots were probed with the L1 probe and a GAPDH probe. The position of the L1 mRNA is indicated. +, present; −, absent. (C) Results from RT-PCR with primers HCMVS and L1a(M) (see panel A) on cytoplasmic RNA extracted from HeLa cells transfected with pMT22 in the absence or presence of a PTB-expressing plasmid. All bands were cloned and sequenced. The band representing HPV-16 mRNA spliced from CSD4313 to SA5639 is indicated. **, PCR artifact due to mispriming.