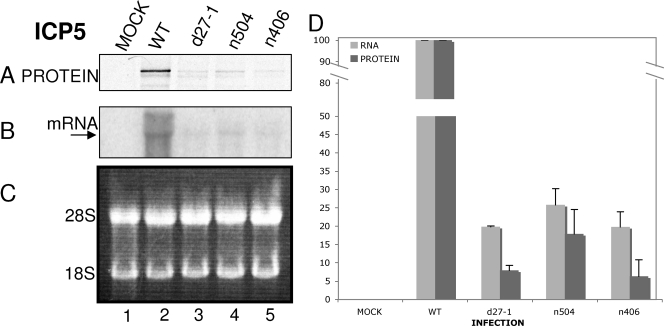
FIG. 4.
ICP5 synthesis rates are decreased in the absence of ICP27, and this effect requires the C terminus of ICP27. Vero cells were either mock infected (lane 1) or infected at an MOI of 20 with HSV-1 WT (lane 2), d27-1 (lane 3), n504 (lane 4), or n406 (lane 5) viruses. Cells were pulse-labeled with [35S]methionine-cysteine (100 μCi/ml) for 30 min at 5.5 hpi and harvested at 6 hpi. Aliquots of cells were lysed or used for RNA isolation as described in Materials and Methods. (A) For protein synthesis analysis, lysates were immunoprecipitated by using a monoclonal antibody to ICP5. Immunoprecipitates were resolved on an SDS-polyacrylamide gel. (B) For mRNA accumulation, the membrane was incubated with a probe specific for ICP5 mRNA, stripped, and rehybridized with a probe specific for GAPDH mRNA (data not shown). (C) Equivalent concentrations of total RNA were resolved on a denaturing formaldehyde agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide. The positions of 28S and 18S rRNAs are indicated on the left of the panel. (D) The levels of ICP5 protein and RNA for mock, HSV-1 WT, d27-1, n504, and n406 infections were quantified relative to the HSV-1 WT infection levels and are represented here as a percentage. The data shown are representative of three experiments.