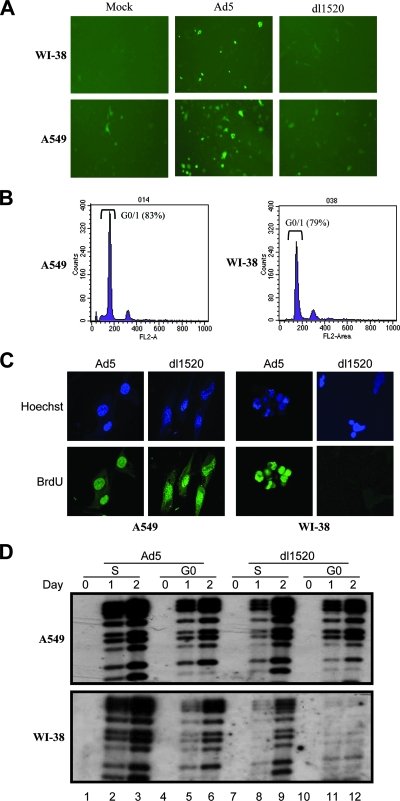
FIG. 5.
(A) The plasmid pCycE-EGFP was transfected into WI-38 and A549 cells, which were then mock infected or infected with Ad5 or dl1520. EGFP expression under the control of the cyclin E promoter was determined 2 days later. Ad5 infection activated the cyclin E promoter and resulted in higher EGFP expression. (B) Cell cycle profiles of A549 and WI-38 cells after incubation in 0.5% serum medium for 2 days. Cells were stained with propidium iodide for FACS analysis. (C) BrdU incorporation into serum-starved quiescent Ad-infected A549 and WI-38 cells. Ad5- and dl1520-infected cells were labeled by 10 mM BrdU for 60 min before fixation at 48 h postinfection. Incorporated BrdU was detected by fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated anti-BrdU monoclonal antibody. Hoechst staining was used to identify nucleus localization. Cells were rinsed with phosphate-buffered saline and analyzed using a fluorescent microscope (Olympus X-70). (D) Southern blotting was used to determine the viral DNA synthesis within A549 and WI-38 cells infected at synchronous G0 versus S phase. The DNA was isolated from the cells at days 0, 1, and 2 postinfection and fragmented with the restriction enzyme PstI. The probe was Ad5 genome DNA.