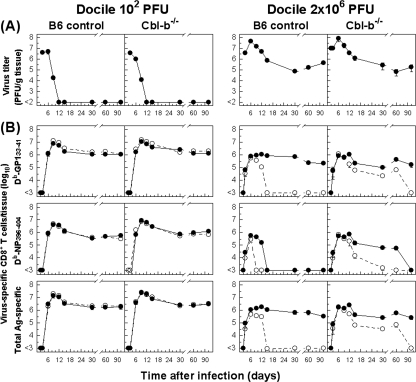
FIG. 1.
Cbl-b inactivation delays virus-specific CD8+ T-cell exhaustion. (A) Cbl-b−/− or B6 mice were infected with 102 or 2 × 106 PFU of LCMV Docile, and virus titers in spleens were measured at the indicated times. Data shown are means ± standard errors of the means (SEM) of log10 PFU/g of tissue for five mice. (B) Parallel total numbers of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells (sums of GP133-41-specific and NP396-404-specific cells indicated as total antigen specific) or specific for GP133-41 or NP396-404 peptide were determined by staining with MHC-I tetramers (•). Virus-specific CD8+ T cells were tested for their ability to produce IFN-γ following stimulation of cells with peptide or with virus-infected DC2.4 cells (○). Data shown are means ± SEM of log10 virus-specific T cells per spleen for 5 to 10 mice.