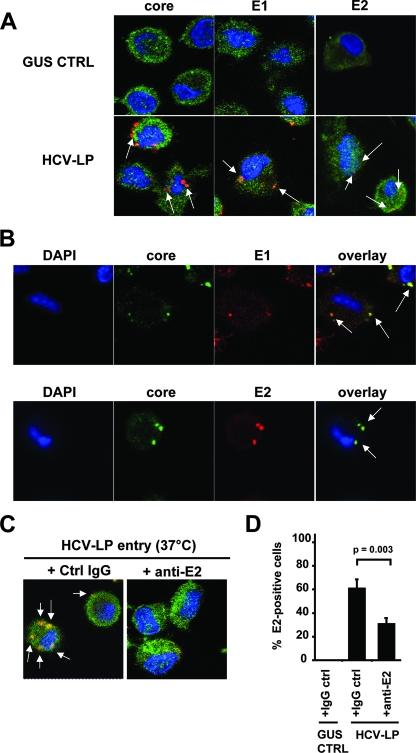
FIG. 7.
HCV-LP uptake into DCs is mediated by envelope glycoprotein E2. (A) HCV-LP uptake by DCs. DCs were incubated with HCV-LPs or insect cell control preparations (GUS) and triple stained for actin (green); viral protein core, E1, or E2 (red); and nucleus (DAPI [4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenylindole], in blue). Arrows indicate viral protein staining. (B) HCV-LPs internalized in DCs. DCs incubated with HCV-LPs were triple stained for nucleus (DAPI, in blue), core (green), and E1 or E2 (red). Overlay of images shows colocalization of core/E1 or core/E2 (right panel). (C) HCV-LP uptake by DCs is mediated by envelope glycoprotein E2. HCV-LPs were preincubated (1 h at 37°C) with anti-E2 antibody (AP33; 50 μg/ml) or control IgG (50 μg/ml) before incubation with DCs. HCV-LP-anti-E2 complexes were then added to DCs and incubated at 37°C for 3 h. Following fixation, DCs were triple stained for actin (green), E2 (red), and nucleus (DAPI, in blue). (D) Quantitation of HCV-LP uptake in the presence and absence of anti-E2 antibody. HCV-LP uptake by DCs in the presence of anti-E2 MAb or control IgG is shown as percentage of cells with positive intracellular HCV-LP E2 staining relative to the total number of cells. The means ± standard deviations of the results from three independent experiments are shown. Statistical analysis was performed by Student's t test.