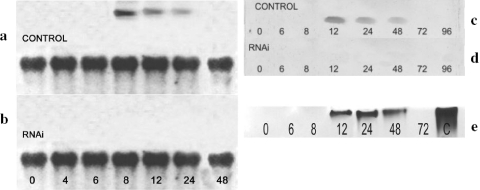
FIG. 2.
Analyses of glycogen phosphorylase expression during encystation. (a and b) Northern blot analysis of glycogen phosphorylase expression during encystation in siRNA-treated (b) and control (a) cultures of Acanthamoeba. Total RNA extracted at different time points during encystation was electrophoresed at 80 V, blotted onto a nylon membrane, and probed with cDNA for glycogen phosphorylase. Top lanes, total RNA hybridized with cDNA corresponding to the catalytic domain of Acanthamoeba glycogen phosphorylase. Bottom lanes, hybridization with 18S mRNA as a control. Numbers indicate the hours after the induction of encystation. (c and d) Western blot analysis of glycogen phosphorylase during encystation in siRNA-treated (d) and control (c) cultures of Acanthamoeba. Protein extracts from different time points during encystation were incubated with polyclonal anti-human glycogen phosphorylase (BB) rabbit antibody, and results were developed with digoxigenin. Numbers indicate the hours after the induction of encystation. (e) Analysis of glycogen phosphorylase activity during encystation of Acanthamoeba. Proteins were isolated in time course experiments and separated by nondenaturing PAGE on a gel containing glycogen. Zymograms were developed by iodine staining of polyglucan synthesized from glucose-1-phosphate. Numbers indicate the hours after the induction of encystation. Lane C, positive control with glycogen phosphorylase b from rabbit muscle.