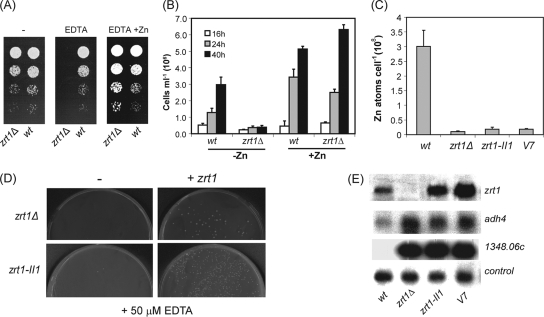
FIG. 6.
(A) Wild-type (wt) and zrt1Δ strains were grown to exponential phase, subjected to fivefold serial dilutions, and spotted onto YE5S agar supplemented with EDTA (200 μM) and ZnSO4 (200 μM) as indicated. Plates were incubated at 30°C for 2 days. (B) Wild-type and zrt1Δ strains were precultured in CSD medium and then inoculated into CSD medium (−Zn) or CSD medium supplemented with 20 μM ZnSO4 (+Zn). Cultures were incubated at 30°C, and cell titers were determined at the indicated time points. Shown are the mean values from three experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (C) Total cellular zinc contents of the indicated strains were measured by atomic absorption spectrometry. Shown are the mean values from three experiments. Error bars indicate standard deviations. (D) Complementation of zrt1− mutants. Cultures of the zrt1Δ strain and zrt1-II1 were transformed with carrier DNA (−) or with carrier DNA and a DNA fragment containing the zrt1+ open reading frame (+ zrt1). Cells were plated onto EMM agar plates supplemented with EDTA (50 μM) and incubated at 30°C for 3 to 4 days. (E) Total RNA was prepared from the indicated strains and subjected to RNA blot hybridization using his3+ (control), zrt1+, adh4+, and SPBC1348.06c probes.