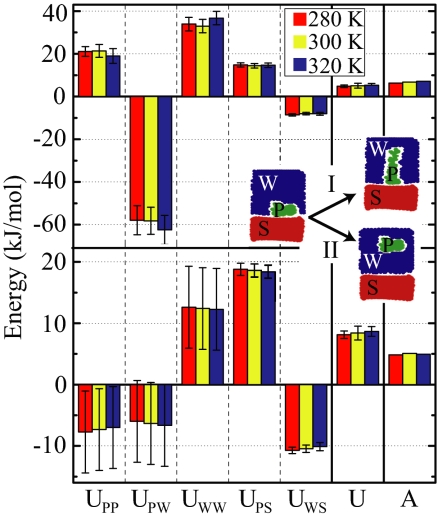
Fig. 6.
Decomposition of the total internal energy per monomer, U, into the contributions from interactions between peptide (P), surface (S), and water (W) for three different temperatures and compared with the free energy A. The upper histogram gives the energy price for desorbing peptide fragment 3 into a stretched conformation (process I), as applicable to AFM experiments, and the lower histogram has the totally relaxed and solvated peptide conformation as the reference state, as applicable to equilibrium adsorption from a bulk solution (process II). In both cases, the various internal energy contributions are larger in magnitude than the total internal energy U.