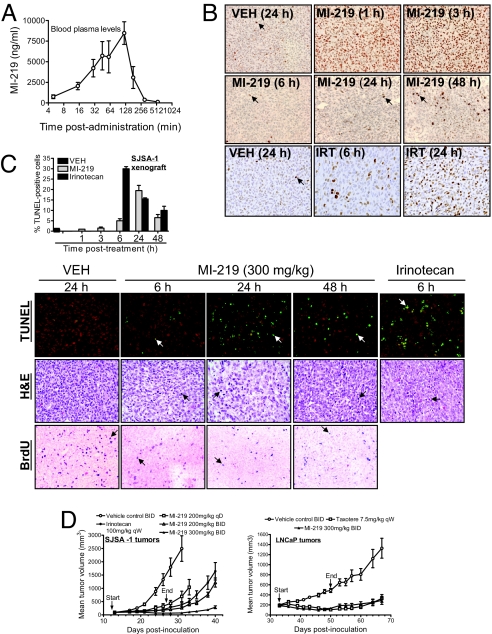
Fig. 4.
MI-219 activates p53 in vivo, inhibits cell proliferation, induces apoptosis in tumor tissues, and achieves robust in vivo anti-tumor activity. (A) A single oral dose of MI-219 (50 mg/kg) was given to mice, and MI-219 concentrations in blood plasma were analyzed by LC/MS/MS. Error bars represent SD of data from three animals. (B) Mice (two to three mice per group), bearing established SJSA-1 xenograft tumors, were treated with a single oral dose of MI-219, irinotecan (IRT), or vehicle, and p53 in tumor tissues was analyzed by IHC staining. Arrows indicate a small fraction of p53-positive cells. A wide-spread p53 staining is observed at 1 and 3 h of treatment with MI-219. (C) SJSA-1 xenograft tumor tissues, harvested from mice treated with a single oral dose of MI-219, were examined for cell proliferation by IHC staining of BrdU and apoptosis by TUNEL and H&E staining. Arrows indicate the positivity of the BrdU and TUNEL staining. H&E shows apoptotic cells with nuclear condensation/fragmentation. To score apoptosis, at least 1,000 cells were analyzed for TUNEL staining. (D) Nude mice (8–10 per group), bearing s.c. SJSA-1 and LNCaP xenograft tumors, were administered with MI-219 (p.o.), irinotecan (i.p.), Taxotere (i.v.), or vehicle control (p.o.). Data are represented as mean tumor volumes ± SEM.