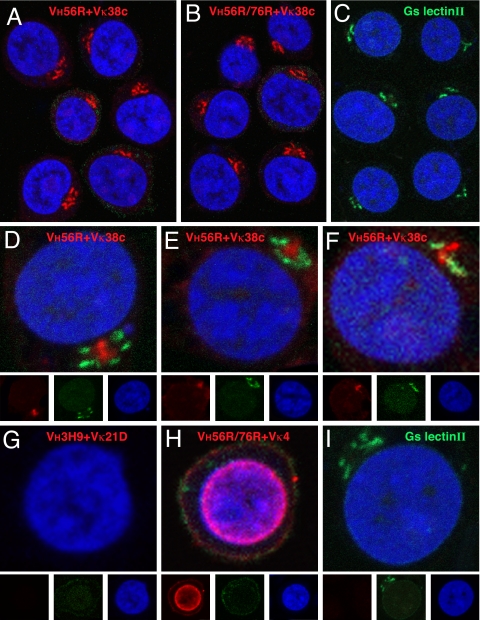
Fig. 3.
Analysis of scFv binding to Jurkat cells. scFv binding to fixed and permeabilized cells was visualized with Alexa Fluor 647 rabbit anti-mouse IgG (displayed in red) and nuclei with Sytox Orange (blue). The VH56R+Vκ38c (A) and VH56R/76R+Vκ38c (B) scFv bind to a perinuclear domain composed of tubular bundles and lamellar stacks that likely corresponds to the Golgi apparatus. Binding of Alexa Fluor 488 lectin II (green) identifies terminal GlcNAc moieties that are enriched in the Golgi (C). The VH56R+Vκ38c scFv is surrounded by lectin II-reactive domains (D–F). VH3H9+Vκ21D scFv does not bind to Jurkat cells (G), whereas VH56R76R+Vκ4 scFv binds predominantly to the nucleus (H). (I) Image of lectin II binding. Separate RGB channels are shown at one-third size below the composite color images for D–I. Binding of scFv to Jurkat cells was indistinguishable from the binding to mouse thymocytes.