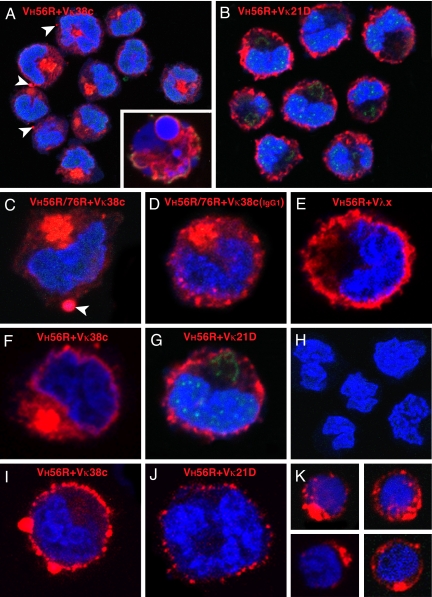
Fig. 4.
Distribution of IgM in B cell hybridomas and primary B cells. VH56R+Vκ38c (A) and VH56R+Vκ21D (B) hybridoma cells were fixed, permeabilized, and incubated with Alexa Fluor 647 goat anti-mouse IgM (red), Alexa Fluor 488 lectin II (green), and Sytox Orange (blue). The VH56R+Vκ38c IgM accumulate inside the cell (A). Cultures of VH56R+Vκ38c contain cells with fragmented nuclei and apoptotic phenotype (Inset). In contrast, VH56R+Vκ21D IgM are localized on or close to the cell surface, and little or no Ig is retained inside the cell (B). (C and F) Individual cells producing VH56R/76R+Vκ38c (C) or VH56R+Vκ38c (F) IgM. Arrowheads in A and C indicate IgM clusters at the cell surface. (D) Hybridoma expressing VH56R/76R+Vκ38c IgG1 shows a similar intracellular accumulation of the Ig but smaller clusters at the plasma membrane. Individual VH56R+Vλx (E) and VH56R+Vκ21D (G) hybridoma cells show IgM receptors that are distributed at or near the cell surface. Cells that have lost expression of IgM do not bind to the goat anti-mouse Abs (H). VH56R+Vκ38c hybridomas that were incubated with anti-mouse IgM, then fixed and stained with Sytox orange, show cell surface clusters of IgM (I). VH56R+Vκ21D hybridomas, when treated the same, show reduced levels of surface IgM (J). B cells from the spleen of a VH56R mouse that were sorted for low surface IgMa, then grown in culture for 48 h, fixed, and stained as in A, show cytoplasmic IgM aggregates (K). Discrete clusters of IgM appear at the cell surface. Thus, the IgM distribution in 35% of primary B cells is strikingly similar to the IgM distribution in VH56R+Vκ38c hybridomas.