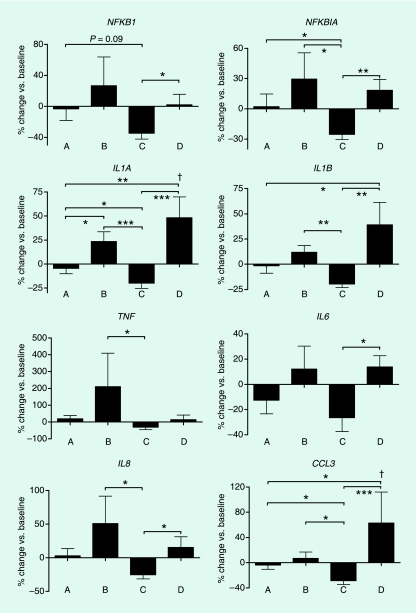
FIGURE 1.
Influence of hyperinsulinaemia and/or hyperglycaemia on proinflammatory mRNA levels. Six subjects were studied on four separate occasions: during a lower insulinaemic euglycaemic (LinsuEgluc) clamp (A), a hyperinsulinaemic euglycaemic (HinsuEgluc) clamp (B), a lower insulinaemic hyperglycaemic (LinsuHgluc) clamp (C) and a hyperinsulinaemic hyperglycaemic (HinsuHgluc) clamp (D). Whole blood obtained at T = 0 and T = 6 h was stimulated for 2 h with lipopolysaccharide. White blood cells were analysed for mRNA levels relative to mRNA levels of the B2M household gene. Data are the mean (± sem) changes in mRNA level ratios at the end of the clamps relative to the change detected at baseline. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001; †P < 0.05 for interaction of hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinaemia.