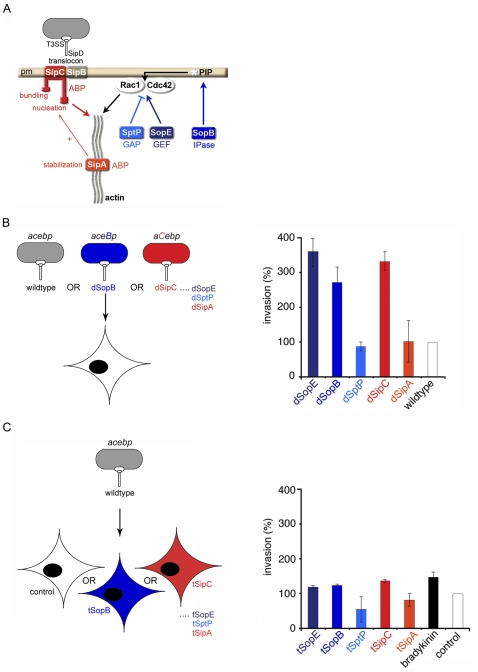
Figure 1. Only T3SS-delivered effectors influence bacterial invasion rate.
A. Salmonella effectors that subvert host cytoskeletal dynamics. Effectors are delivered into the host cell via the type III secretion system (T3SS). Effector delivery requires Salmonella invasion proteins SipB and SipC, which form a plasma membrane-integral translocon likely linked to the T3SS by SipD. Two delivered effector Sips are actin-binding proteins (ABPs) that modulate actin dynamics: SipC nucleates actin polymerization and cross-links (bundles) actin filaments (F-actin) at the cell plasma membrane (pm), activities stimulated by SipA, which independently binds F-actin and inhibits filament depolymerization. Three further effectors are delivered into the cell via a SipB-SipC-dependent mechanism: the GDP-GTP exchange factor (GEF) SopE (or ubiquitous SopE2) activates Cdc42 and Rac1 Rho-family GTPases; the inositol polyphosphatase (IPase) SopB indirectly activates these GTPases and RhoG via inositol phosphate (PIP) hydrolysis; the antagonistic GTPase activating activity (GAP) and tyrosine phosphatase activities of SptP inactivate signaling after bacterial entry. B. Left: Schematic illustrating infection of cultured cells by wild-type or effector-augmented S.typhimurium strains. Wild-type bacteria endogenously express, secrete and deliver sipA, sipC, sopE, sopB and sptP (abbreviated to acebp). Effector-augmented strains each express, secrete and deliver mildly increased levels of an individual plasmid-encoded effector in the wild-type background [enhanced effector shown in capitals, e.g. aceBp (dSopB) and aCebp (dSipC) produce increased levels of SopB and SipC, respectively]. Right: Graph comparing relative cell invasion rates of wild-type and effector-augmented (denoted d-effector) S.typhimurium strains. Invasion was compared to wild-type after 60 min (assigned as 100%). Results are mean±SEM of 4 independent experiments each performed in triplicate. C. Left: Schematic illustrating infection of effector-transfected cells by S.typhimurium. Wild-type bacteria endogenously express, secrete and deliver sipA, sipC, sopE, sopB and sptP (abbreviated to acebp). Cultured cells were transfected with individual effectors prior to infection (denoted t-effector). Right: Graph comparing invasion of mock transfected (control), effector-transfected (t-effector) or bradykinin-treated cells by wild-type S.typhimurium. Invasion was compared to wild-type after 60 min (assigned as 100%). Results are mean±SEM of 4 independent experiments each performed in triplicate.