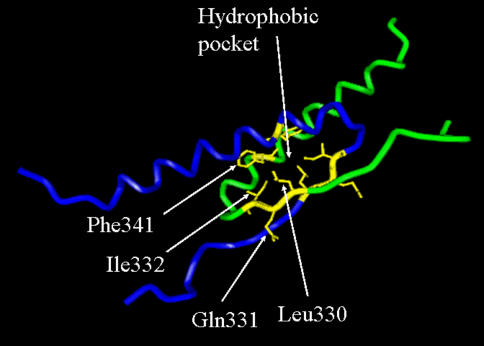
Fig. 3.
Human p53 tetramerization domain. Interacting regions of two p53 monomers (peptide backbones visualized in green and blue) which form a dimer. A second identical dimer (not shown) mates with the first to form the final assembled protein. Side chains of the three residues tested in this work, Leu330, Gln331 and Ile332, and the side chain of Phe341 are highlighted. R-groups of Leu330, Ile332 and Phe341 are oriented toward each other and form a portion of the hydrophobic pocket, which stabilizes the p53 tetramer