Figure 2. Example of the effects of force application on inspiratory intercostal activity.
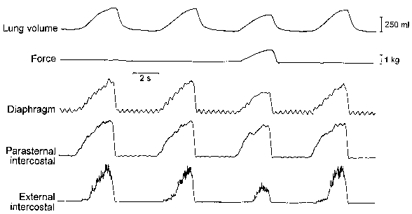
Traces obtained in a representative animal. The parasternal intercostal and external intercostal muscles (third intercostal space) were electrically active with the diaphragm during the inspiratory phase of the breathing cycle. When force was applied on the central tendon, the external intercostal EMG activity was reduced markedly and the parasternal intercostal activity was reduced moderately. Tidal volume was also reduced.
