Figure 5. Prolonged exposure to PGF on tension, membrane potential and interval between spontaneous activity in term human uterine smooth muscle.
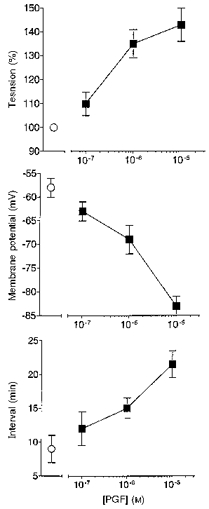
Ten spontaneously active tissues at weeks 37–39 of pregnancy were exposed to 10−7, 10−6 or 10−5 M PGF (2–3 concentrations per tissue), each for 30–180 min. The peak amplitude of the rise in tension, the most negative level of membrane potential attained and interval between action potentials and rises in tension during PG exposure were recorded (▪) (data from 6–7 tissues at each point). The values of these parameters in the same tissues prior to application of PGF are also shown (^).
