Figure 2. Action potential waveforms.
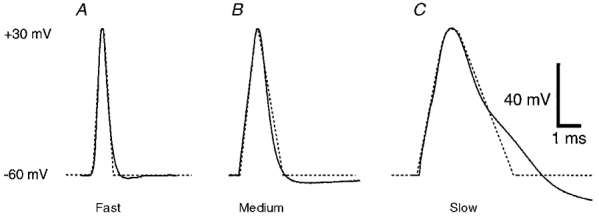
To create the fast, medium, and slow model AP waveforms, three natural APs (continuous lines) of different durations were used. APs were adapted from the presynaptic terminal of the calyx of Held (A), the presynaptic Xenopus motoneurone varicosity (B) and the soma of a chick ciliary ganglion neurone (C). To facilitate the use of these as voltage-clamp commands, the rising phase was modelled using a series of ramps (dotted lines), and the falling phase was simplified to a single ramp to allow consistent alterations in the repolarization phase. The APs were normalized to a resting potential of -60 mV and a peak amplitude of +30 mV.
