Figure 3. BzATP induces a transmembrane Ca2+ influx.
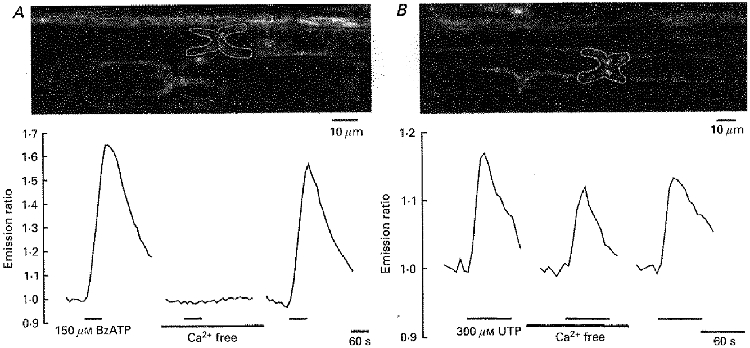
A, the white outline in the upper panel shows a paranodal Schwann cell region within an isolated rat spinal root stained with the Ca2+-sensitive dyes Calcium Green-1 and Fura Red. Changes in [Ca2+]i were measured during application of BzATP (150 μM) into the standard and into a Ca2+-free bathing solution. B, a similar experimental protocol was applied to a different rat spinal root. In this case, changes in [Ca2+]i were measured during application of UTP (300 μM) into the standard and into a Ca2+-free bathing solution. Note that only the BzATP-induced intracellular Ca2+ transient was completely and reversibly blocked during removal of extracellular Ca2+.
