Figure 3. Blockade of the residual synaptic current by nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonists.
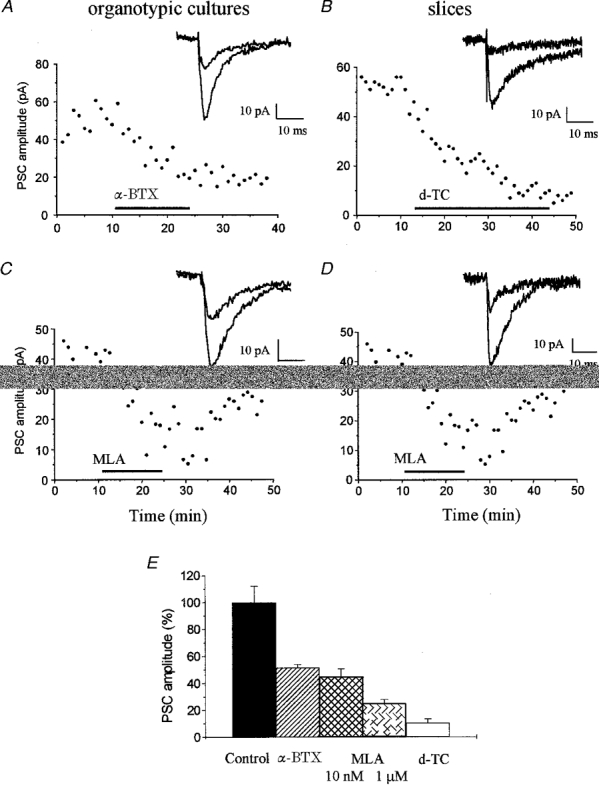
All experiments illustrated in this figure were carried out in the continuous presence of NBQX (5 μM), R-CPP (20 μM) and bicuculline (20 μM). Experiments on the left were carried out on organotypic cultures and on the right on acutely dissected hippocampal slices. A, illustration of an experiment made with an organotypic slice culture showing the irreversible blockade of the residual current produced by application of α-BgTX (200 nM, in serum bovine albumin at 20 mg ml−1). The responses illustrated on the right were recorded before and during application of α-BgTX. B, experiment made on a hippocampal slice showing the blockade of the residual current produced by 20 μM d-tubocurarine. C and D, illustration of the effect of 10 nM MLA, a nicotinic receptor antagonist, on the residual current recorded in an organotypic culture (C) and hippocampal slice (D). The traces on the right were recorded before and during application of MLA. E, bar graph summarizing the effects of MLA (10 nM and 1 μM), α-bungarotoxin (200 nM) and d-tubocurarine (20 μM) on the peak amplitude of the residual current recorded in organotypic cultures. Data are mean ±s.e.m. of 3–5 experiments. Drug effects were measured 15 min after application. Differences from control are statistically significant (P < 0.01, Student's t test).
