Figure 6. Ba2+ inhibition of inward rectifier potassium currents in Xenopus oocytes injected with RNA encoding Kir2.1 cloned from vascular smooth muscle cells.
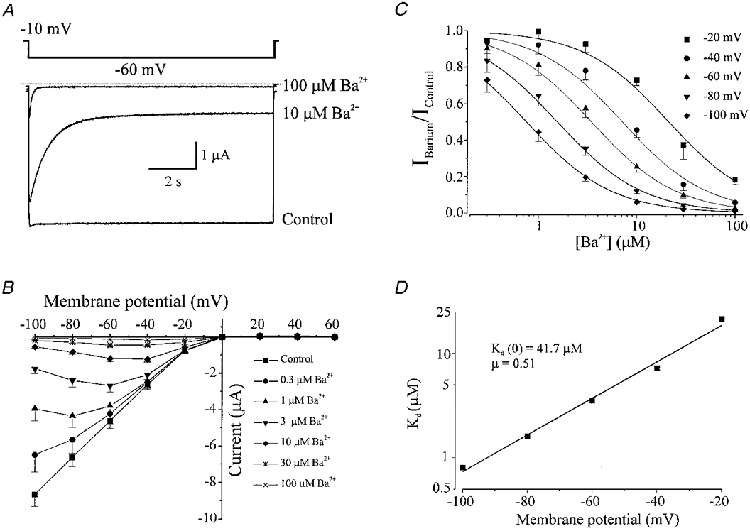
Membrane current recorded from the same oocyte with voltage steps from a holding potential of −10 mV to −60 mV in the presence of 0 (control), 10 and 100 μM Ba2+. External K+ was 90 mM. Dotted line indicates zero current level. B, current-voltage relationship demonstrating the effect of applying 0.3, 1, 3, 10, 30 and 100 μM Ba2+ on membrane currents recorded at the end of 10 s voltage pulses (n = 5). Bathing K+ was 90 mM. C, relationship between external Ba2+ concentration and the fractional inhibition of inward current at −20, −40, −60, −80 and −100 mV. Data were fitted with eqn (1), to give Kd values of (μm): 21.4, 7.2, 3.5, 1.6 and 0.8 at −20, −40, −60, −80 and −100 mV, respectively. D, voltage dependence of the dissociation constants (Kd) from C. Data were fitted with eqn (2) with a Kd at 0 mV of 41.7 μM, and a slope (μ) of 0.51.
