Figure 5. A dephosphorylating treatment interrupted cell-to-cell communication.
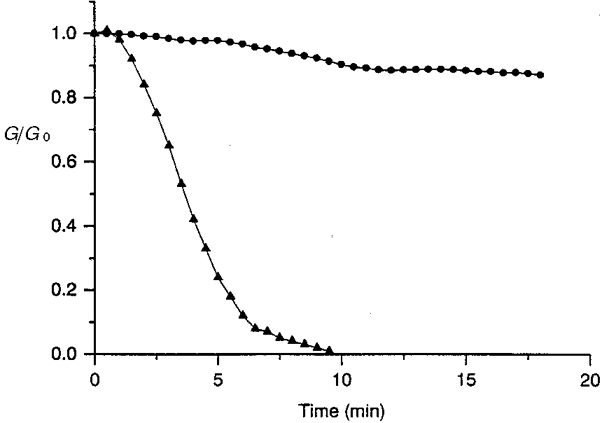
When a non-specific dephosphorylating enzyme (alkaline phosphatase, 10 U ml−1) was intracellularly applied, the junctional conductance, presented in units of the original conductance, 28 (•) and 32 nS (▴), progressively declined and led to complete interruption of intercellular communication (▴); in contrast, in the presence of an inhibitor of alkaline phosphatase activity (β-glycerophosphate, 50 mM, •), the main part of the intercellular coupling was preserved. Similar results were obtained in each of 9 (▴) and 8 (•) myocyte pairs.
