Figure 2. The effects of forskolin and IBMX on the activity and Ser943 phosphorylation of NKA at both low and high [Ca2+]i.
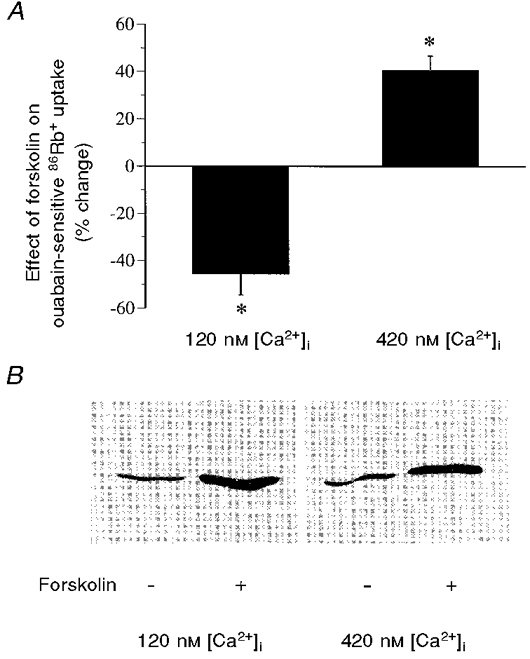
Confluent cultures of COS cells expressing rat renal NKA were treated with forskolin (10−5 M) and IBMX (5 × 10−4 M) for 15 min at 37 °C. Following drug treatment, both the activity and Ser943 phosphorylation of NKA were assayed. The levels of [Ca2+]i were measured in a SPEX dual-beam excitation spectrofluometer using fura-2 AM as an indicator. An increase in [Ca2+]i was achieved by preincubation of cells with the Ca2+ ionophore A23187 (10−5 M). The [Ca2+]i values shown here represent the mean values of the [Ca2+]i from 16-21 individual cells in four separate experiments, which were calculated based on an in vivo calibration system (see Methods). A, the effect of forskolin and IBMX on the activity of NKA, which was measured as ouabain-sensitive 86Rb+ uptake. Values are means ±s.e.m. of 5 separate experiments. The basal NKA activity (in nmol mg−1 min−1) was 18.75 ± 2.10 at low [Ca2+]i and 20.62 ± 2.53 at high [Ca2+]i. B, the effect of forskolin and IBMX on the state of Ser943 phosphorylation, which was determined by Western blot analysis with an antibody specifically recognizing the Ser943-phosphorylated, but not the dephosphorylated, form of NKA. A blot representative of 3 experiments is shown. *P < 0.01.
