Figure 2. Dose-dependent inhibition of the Na+ currents by 8,9-EET (A) and arachidonic acid (B).
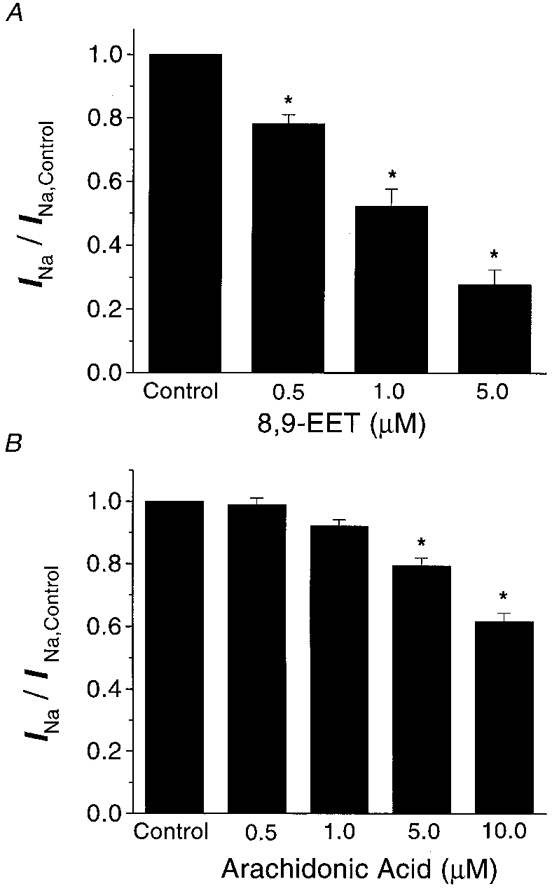
A shows the magnitude of Na+ current inhibition by 0.5, 1.0 and 5.0 μM 8,9-EET as a ratio of Na+ currents under control conditions. Na+ currents were evoked from a resting potential of −80 mV to a test potential of −30 mV (n = 10, *P < 0.05vs. control). B shows the magnitude of Na+ current inhibition by 0.5, 1.0, 5.0 and 10.0 μM arachidonic acid as a ratio of control Na+ currents under conditions similar to those shown in A (n = 11, * P < 0.05).
