Figure 1. Discharges of motor cortex neurones recorded extracellularly via chronically implanted microwire electrodes.
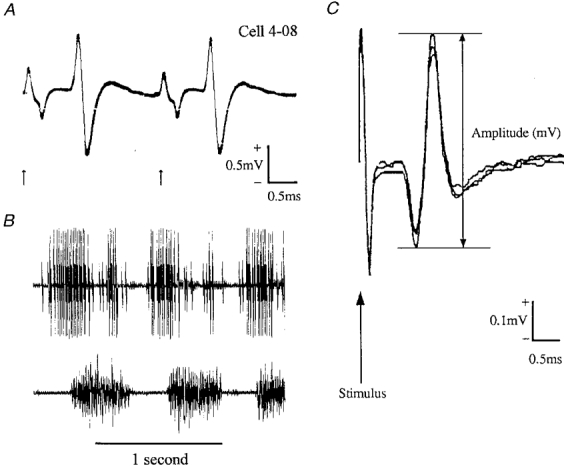
A, example of a neurone (a fast axon PTN) generating antidromic action potentials in response to each of two 0.2 ms stimuli applied to the pyramidal tract (arrows); interstimulus interval, 2.4 ms; 10 trials superimposed. B, the PTN discharged rhythmically during ladder walking. Locomotor EMG signals from the lateral head of triceps brachii muscle (an elbow extensor with one period of activity per step during stance) in the contralateral forelimb were recorded simultaneously. The neurone discharged two high frequency bursts of impulses per step cycle (a second, smaller and discriminable cell discharged when the larger unit was silent). C, three consecutive NCAPs superimposed to illustrate variation in peak-to-peak amplitude.
