Figure 2. Respiratory and blood pressure responses to repeated hypoxia in sleep.
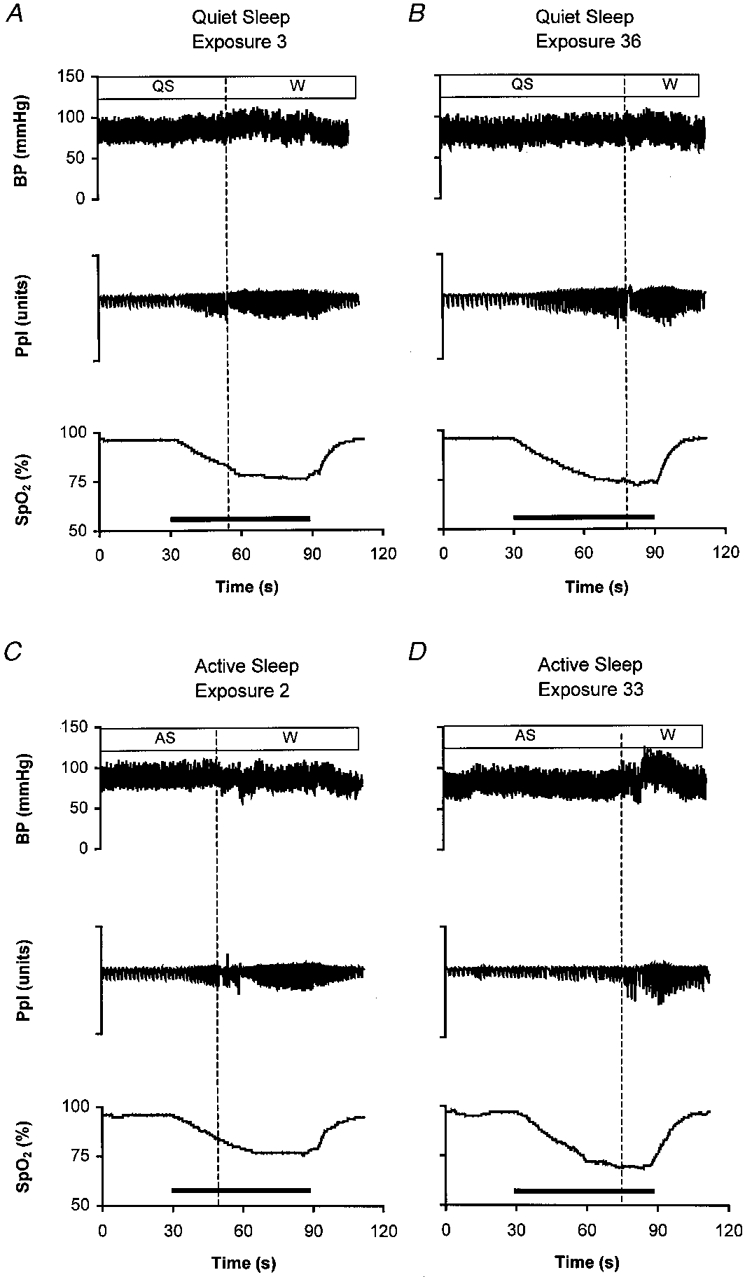
Physiological recordings in a sleeping lamb during periods of quiet sleep (QS) and active sleep (AS) during repeated exposures to hypoxia (horizontal bar). Arousal to the waking state (W) is signified by the vertical dotted line. BP, arterial blood pressure (mmHg); Ppl, pleural pressure (arbitrary units); Sp,O2, pulse oxygen saturation (as a percentage). The hypoxia stimulus, induced by rapidly changing the air in the inspiratory line to a gas mixture of Fi,O2= 0.10, Fi,CO2= 0.03 in N2, is denoted by the horizontal bar. Animals were exposed to a series of 40 repetitions of hypoxia during sleep; the number of each illustrated exposure in the series is indicated on each panel. During QS, progressive increases of ventilatory amplitude (Ppl) and BP occur up to the point of arousal. Note that the cardio-respiratory responses in QS are similar early (A) and late (B) in the series of exposures to hypoxia. During AS, by contrast, the progressive increases in ventilation and blood pressure that occur up to the point of arousal early in the series of exposures (C) are depressed during later exposures (D).
