Figure 5. Effects of treatment with both ω-conotoxin MVIIA and ω-conotoxin SVIB on the responses elicited by α,β-methylene-ATP and 2-methyl-5-HT.
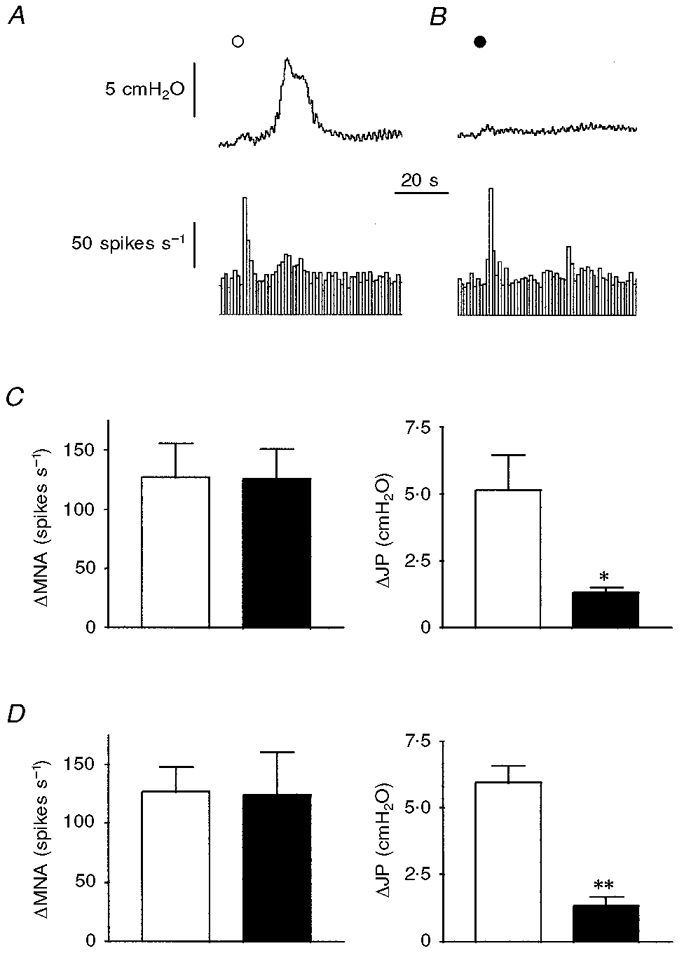
A, administration of α,β-methylene-ATP (^; 30 μg kg−1, i.a.) evoked an increase in intrajejunal pressure (upper trace) and a rapid burst of afferent discharge (lower trace) followed by a later burst which corresponded temporally with the pressure elevation. B, after treatment with ω-conotoxin MVIIA and ω-conotoxin SVIB (each at 25 μg kg−1, i.v.) for 5 min, the early burst of afferent activity elicited by α,β-methylene-ATP (•; 30 μg kg−1, i.a.) was unaffected whereas the elevation in intrajejunal pressure and concomitant afferent activity were abolished. C and D, summarised data of the peak effects of α,β-methylene-ATP (30 μg kg−1, i.a.) and 2-methyl-5-HT (10 μg, i.v.), respectively, on afferent discharge and intrajejunal pressure before (□) and after (▪) treatment with the conotoxins. Note that only the peak increase in intrajejunal pressure evoked by either α,β-methylene-ATP (C) or 2-methyl-5-HT (D) was affected after treatment with toxin. The bars in C and D represent means ±s.e.m. for 4 experiments. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, significant difference between magnitude of response before and after toxin treatment. For abbreviations, see Fig. 1.
