Figure 2. Effects of different exogenous Ca2+ chelators on islet glucose-induced insulin release.
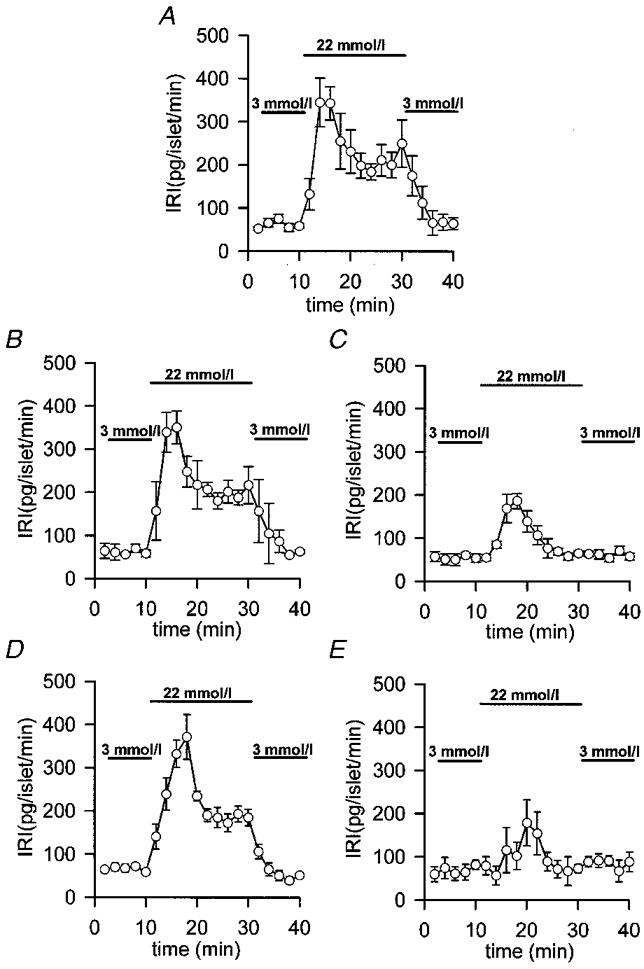
Islets were loaded for 1 h at 37 °C in modified Krebs buffer with 100 μmol l−1 of the different exogenous chelators in AM form. Then, batches of 10 islets were perifused at a flow rate of 1 ml min−1 at 37 °C with fresh modified Krebs buffer supplemented with 1 % bovine serum albumin. After a 30 min stabilization period with 3 mmol l−1 glucose, the islets were perifused for 10 min with 3 mmol l−1 glucose, then for 20 min with 22.2 mmol l−1 glucose and finally for 10 min with 3 mmol l−1 glucose. A, unloaded control islets. B, 100 μmol l−1 EGTA-loaded islets. C, 100 μmol l−1 BAPTA-loaded islets. D, 100 μmol l−1 Calcium Orange-5N-loaded islets. E, 100 μmol l−1 Calcium Green-5N-loaded islets. Insulin was assayed by radioimmunoassay and determinations were run in triplicate (IRI, immunoreactive insulin). Values are expressed as means ±s.e.m. of 7 experiments. Bars represent the addition of the different glucose concentrations.
