Figure 2. Effect of DHA on the voltage dependence of activation in an adult rat ventricular myocyte.
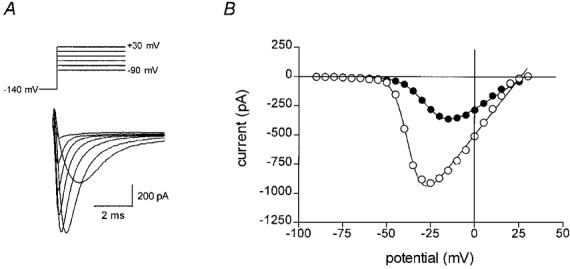
A, sodium currents were evoked by voltage steps from a holding potential of −140 mV to various voltages between −90 mV and +30 mV as depicted (upper panel). Plotted below are superimposed currents evoked at −40, −30, −20, −10, 0, 10 and 20 mV. B, the peak current amplitude was plotted against the pulse potential. Typical data are shown as points representing control (^) or in the presence of 25 μM DHA (•). The continuous line shows the least squares best fit of eqn (1). The parameters for the best fit in each case were: control, Gmax = 19.3 nS, V′ = −37.2 mV, k = 4.17 mV−1 and Erev = 25.9 mV; and in the presence of 25 μM DHA, Gmax = 9.6 nS, V′ = −26.2 mV, k = 6.43 mV−1 and Erev = 29.0 mV, where Gmax is the maximum conductance, V′ is the voltage at which 50 % of the channels are activated, k is the slope factor for the voltage dependence of activation and Erev is the reversal potential.
