Figure 6. Preventing Ca2+ entry through the cation channel protects from CtVm-induced refractoriness.
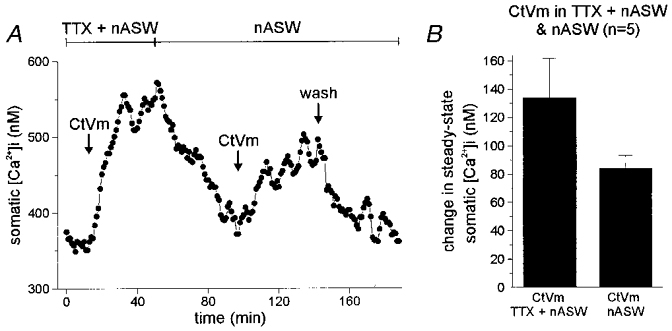
A, CtVm responses in TTX-containing nASW followed by application in nASW alone. Applying 100 μg ml−1 CtVm in nASW containing 100 μM TTX resulted in an ∼175 nM rise in [Ca2+]i. Subsequent wash out of both CtVm and TTX produced a recovery of [Ca2+]i levels to near control. When the neurone was exposed to CtVm again, but now in nASW alone, the [Ca2+]i was elevated a second time, by ∼75 nM. B, the average data for 5 such experiments shows that application of CtVm in TTX protected the bag cell neurones from refractoriness, as the second application of CtVm in nASW consistently produced an elevation of [Ca2+]i, unlike the data of Fig. 4A and B.
